[Oracle-Sql] C.12 Group Functions
Categories: Oracle-Sql
Tags: Group Functions
📋 This is my note-taking from what I learned in the class “Introduction To Database Concept”
- Reference link - SQL Oracle Function: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/functions001.htm
Group Functions
- Return one result per group of rows processed
- Are also called multiple-row and aggregate functions
- All group functions ignore
NULLvalues exceptCOUNT(*) - Use
DISTINCTto suppress duplicate values.
Added Clauses
SELECT *|COLUMNNAME, COLUMNNAME, ...
FROM TABLENAME
[WHERE CONDITION]
[GROUP BY COLUMNNAME, COLUMNNAME, ...]
[HAVING GROUP CONDITION];
SUM Function
Calculates total amount stored in a numeric column for a group of rows
SELECT SUM((PAIDEACH-COST) * QUANTITY) "TOTAL PROFIT"
FROM ORDERITEMS JOIN BOOKS USING (ISBN)
WHERE ORDER# = 1007;
AVG Function
Calculates the average of numeric values in a specified column
SELECT AVG(RETAIL-COST) "AVERAGE PROFIT"
FROM BOOKS
WHERE CATEGORY = 'COMPUTER';
COUNT Function
Two purposes:
- Count non-NULL values
- Count total records, including those with NULL values
COUNT Function – Non-NULL Values
Include column name in argument to count number of occurrences
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT CATEGORY)
FROM BOOKS;
COUNT Function – NULL Values
Include asterisk in argument to count number of rows
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM ORDERS
WHERE SHIPDATE IS NULL;
MAX Function
Returns the largest value
SELECT MAX(RETAIL-COST) "HIGHEST PROFIT"
FROM BOOKS;
MIN Function
Returns the smallest value
SELECT MIN(PUBDATE)
FROM BOOKS;
Datatypes
The COUNT, MIN, and MAX functions can be used on values with character, numeric, and date datatypes
Grouping Data
GROUP BY clause:
- Used to group data
- Must be used for any individual column in the SELECT clause with a group function
- Cannot reference column aliases
SELECT CATEGORY, TO_CHAR(AVG(RETAIL-COST), '999.99') "PROFIT"
FROM BOOKS
GROUP BY CATEGORY;
Common Error
A common error is missing a GROUP BY clause for non-aggregated columns in the SELECT clause
SELECT CATEGORY, TO_CHAR(AVG(RETAIL-COST), '999.99') "PROFIT"
FROM BOOKS;
# An error was encountered performing the requested operation:
# not a single-group group function
Restricting Aggregating Output
HAVING clause serves as the WHERE clause for grouped data
SELECT CATEGORY, TO_CHAR(AVG(RETAIL-COST), '999.99') "PROFIT"
FROM BOOKS
GROUP BY CATEGORY
HAVING AVG(RETAIL-COST) > 15;
When included in the same SELECT statement, the clauses are evaluated in the order of:
- WHERE
- GROUP BY
- HAVING
SELECT CATEGORY, TO_CHAR(AVG(RETAIL-COST), '999.99') "PROFIT"
FROM BOOKS
WHERE PUBDATE > '01-JAN-05'
GROUP BY CATEGORY
HAVING AVG(RETAIL-COST) > 15;
Nesting Functions
Inner function is resolved first
SELECT AVG(SUM(QUANTITY * PAIDEACH)) "AVERAGE ORDER TOTAL"
FROM ORDERS JOIN ORDERITEMS USING (ORDER#)
GROUP BY ORDER#;
Maximum nesting depth: 2
Statistical Group Functions
Based on normal distribution
Includes:
- STDDEV
- VARIANCE
STDDEV Function
SELECT CATEGORY, COUNT(*), TO_CHAR(AVG(RETAIL-COST), '999.99') "AVG", TO_CHAR(STDDEV(RETAIL-COST), '999.9999') "STDDEV"
FROM BOOKS
GROUP BY CATEGORY;
VARIANCE Function
Determines data dispersion within a group
SELECT CATEGORY, TO_CHAR(VARIANCE(RETAIL-COST), '999.99') "VAR", MIN(RETAIL-COST) "MIN", MAX(RETAIL-COST) "MAX"
FROM BOOKS
GROUP BY CATEGORY;
Enhanced Aggregation for Reporting
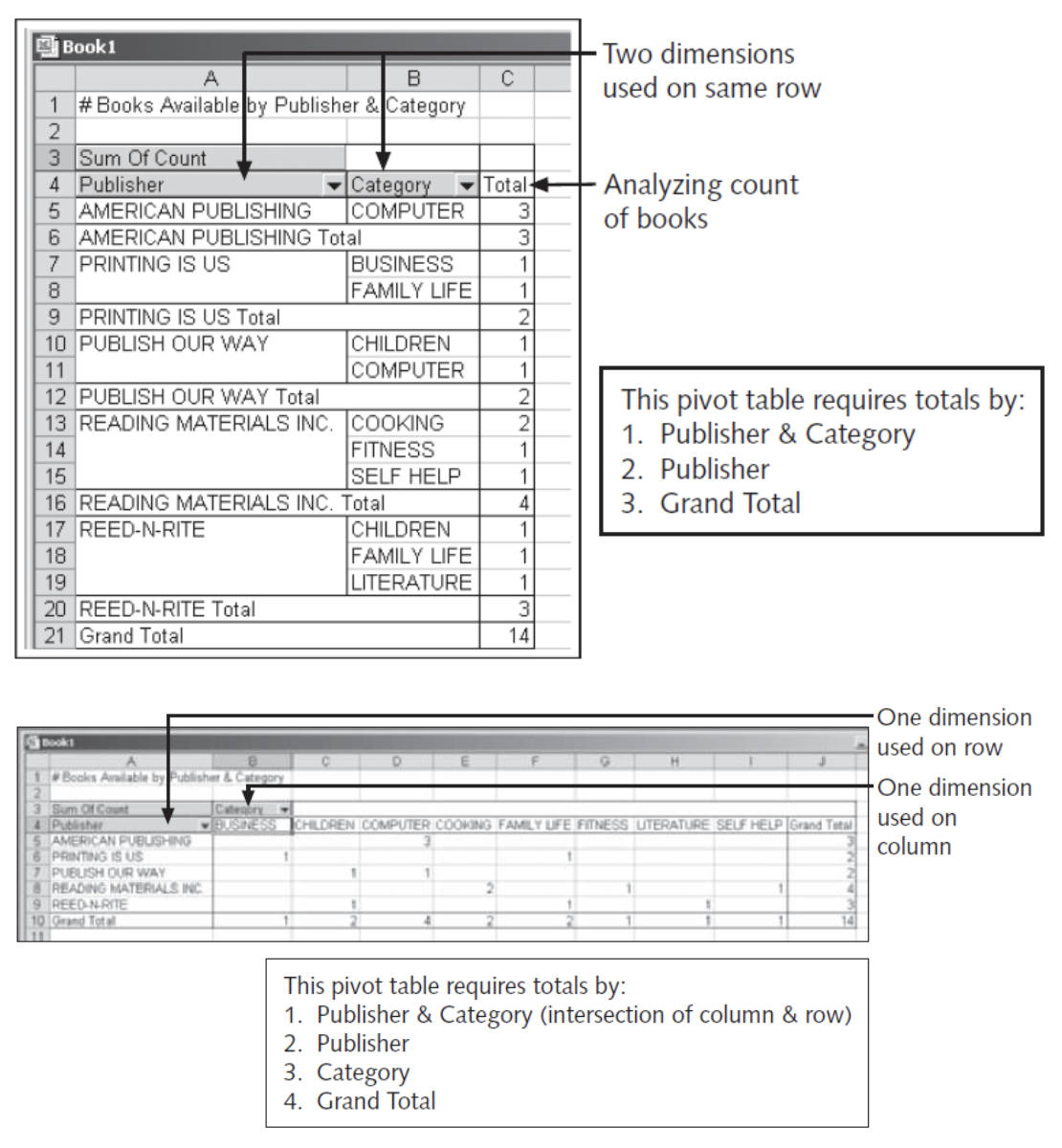
Oracle provides extensions to the GROUP BY clause, which allow both aggregation across multiple dimensions or the generation of increasing levels of subtotals with a single SELECT statement
A dimension is a term used to describe any category used in analyzing data, such as time, geography, and product line
Each dimension could contain various levels of aggregation; for example, the time dimension may include aggregation by month, quarter, and year
Excel Pivot Table Example
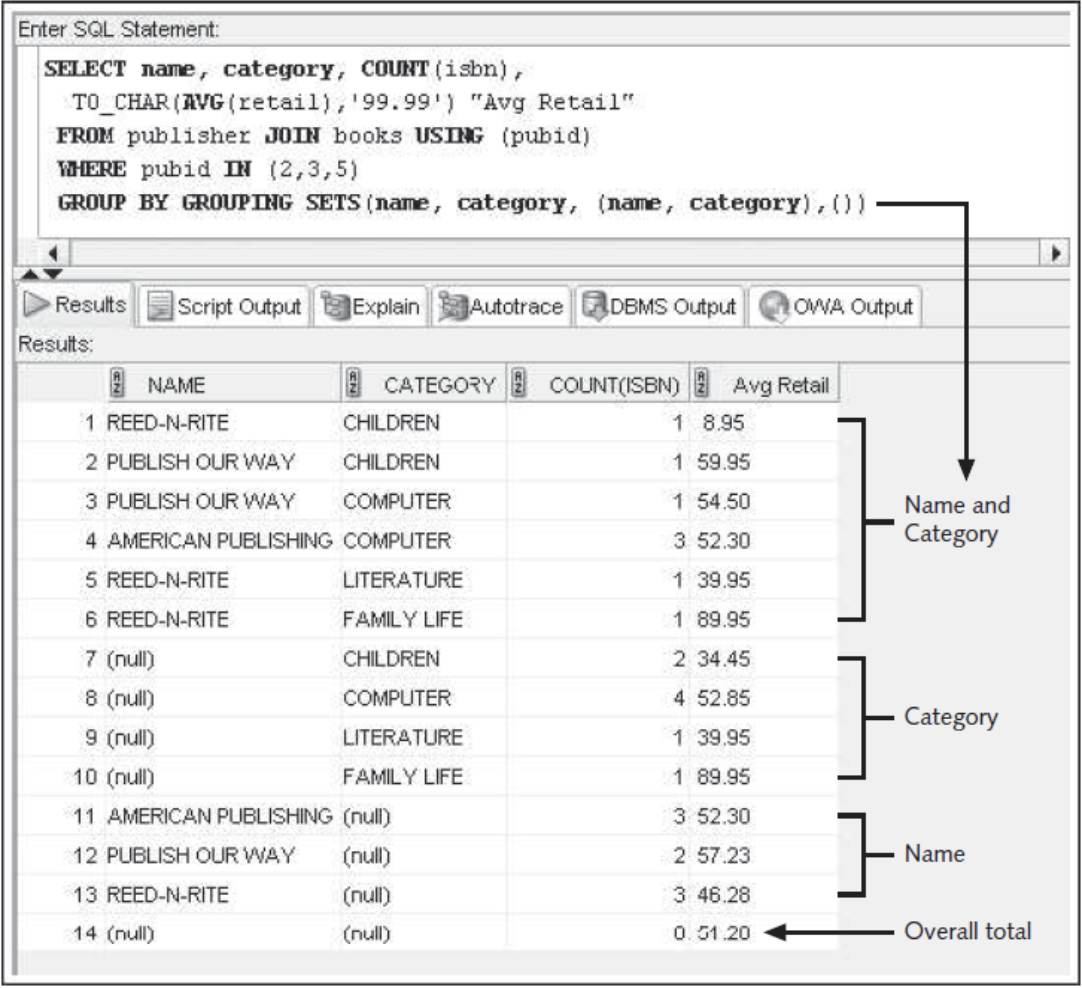
Grouping Sets
SELECT NAME, CATEGORY, COUNT(ISBN), TO_CHAR(AVG(RETAIL), '99.99') "AVG RETAIL"
FROM PUBLISHER JOIN BOOKS USING (PUBID)
WHERE PUBID IN (2,3,5)
GROUP BY GROUPING SETS(NAME, CATEGORY, (NAME, CATEGORY), ());
CUBE
SELECT NAME, CATEGORY, COUNT(ISBN), TO_CHAR(AVG(RETAIL), '99.99') "AVG RETAIL"
FROM PUBLISHER JOIN BOOKS USING (PUBID)
WHERE PUBID IN (2,3,5)
GROUP BY CUBE(NAME, CATEGORY)
ORDER BY NAME, CATEGORY;
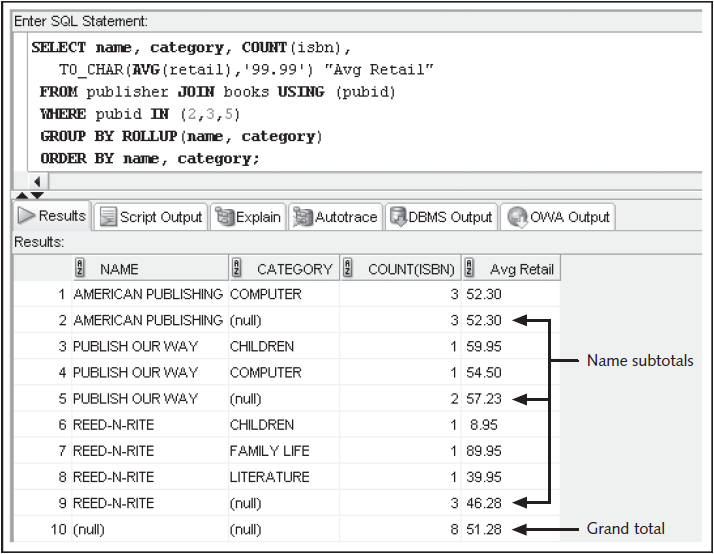
ROLLUP
SELECT NAME, CATEGORY, COUNT(ISBN), TO_CHAR(AVG(RETAIL), '99.99') "AVG RETAIL"
FROM PUBLISHER JOIN BOOKS USING (PUBID)
WHERE PUBID IN (2,3,5)
GROUP BY ROLLUP(NAME, CATEGORY)
ORDER BY NAME, CATEGORY;
PATTERN MATCHING
SELECT *
FROM WEBHITS MATCH_RECOGNIZE (
PARTITION BY WPAGE
ORDER BY WHDATE
MEASURES STRT.WHDATE AS BEGIN_WDATE,
LAST(DOWN.WHDATE) AS LOW_WDATE,
LAST(UP.WHDATE) AS END_WDATE
ONE ROW PER MATCH
AFTER MATCH SKIP TO LAST UP
PATTERN (STRT DOWN+ UP+)
DEFINE
DOWN AS DOWN.TOTAL < PREV(DOWN.TOTAL),
UP AS UP.TOTAL > PREV(UP.TOTAL)
) WH
ORDER BY WH.WPAGE, WH.BEGIN_WDATE;
Summary
- The AVG, SUM, STDDEV, and VARIANCE functions are used only with numeric fields
- The COUNT, MAX, and MIN functions can be applied to any datatype
- The AVG, SUM, MAX, MIN, STDDEV, and VARIANCE functions all ignore NULL values
- By default, the AVG, SUM, MAX, MIN, COUNT, STDDEV, and VARIANCE functions include duplicate values
- The GROUP BY clause is used to divide table data into groups
- If a SELECT clause contains both an individual field name and a group function, the field name must also be included in a GROUP BY clause
- The HAVING clause is used to restrict groups in a group function
- Group functions can be nested to a depth of only two. The inner function is always performed first, using the specified grouping. The results of the inner function are used as input for the outer function
- The STDDEV and VARIANCE functions are used to perform statistical analyses on a set of data
- GROUPING SETS operations can be used to perform multiple GROUP BY aggregations with a single query
- The CUBE extension of the GROUP BY calculates aggregations for all possible combinations or groupings of columns included
- The ROLLUP extension of the GROUP BY calculates increasing levels of accumulated subtotals for the column list provided
- Composite columns and concatenated groupings can be used in GROUPING SETS, CUBE, and ROLLUP operations
- The GROUP_ID function helps eliminate duplicate grouping results
C.12 Demo
SELECT RETAIL-COST FROM BOOKS;
--Returns total value . ignore null values
SELECT SUM(RETAIL-COST) FROM BOOKS;
-- calculate the avg price of cooking books
SELECT AVG(RETAIL-COST) FROM BOOKS WHERE CATEGORY ='COOKING';
SELECT RETAIL-COST FROM BOOKS WHERE CATEGORY ='COOKING';
-- Count number of books .Rows containing NULL values in the field aren�t included in the results.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM books;
SELECT COUNT(shipdate) FROM orders;
select shipdate from orders;
SELECT COUNT(* ) FROM orders;
-- select the highest value. Ignores null values
select customer# from customers ;
SELECT MAX(customer#) from customers;
-- select the lowerst value from the selected field
SELECT MIN(RETAIL-COST) FROM BOOKS;
SELECT CATEGORY,MIN(RETAIL-COST) FROM BOOKS GROUP BY category;
SELECT CATEGORY,MIN(RETAIL-COST) FROM BOOKS group by CATEGORY;
-- Having clause - only for grouping function .
SELECT category,AVG(RETAIL-COST) FROM BOOKS GROUP BY CATEGORY HAVING AVG(RETAIL-COST) >20;
SELECT category,AVG(RETAIL-COST) FROM BOOKS GROUP BY CATEGORY HAVING AVG(RETAIL-COST) >15;
--Enables performing multiple GROUP BY operations with a single query
SELECT name, category, AVG(retail) FROM publisher JOIN books USING(pubid) GROUP BY GROUPING SETS (name, category, (name,category), ());
--Performs aggregations for all possible combinations of columns included.
SELECT name, category, AVG(retail) FROM publisher JOIN books USING(pubid) GROUP BY CUBE(name, category) ORDER BY name, category;
--Performs increasing levels of cumulative subtotals, based on the specified column list
SELECT name, category, AVG(retail) FROM publisher JOIN books USING(pubid) GROUP BY ROLLUP(name, category) ORDER BY name, category;

Leave a comment