[Oracle-Sql] C.1 Overview of Database Concepts
Categories: Oracle-Sql
Tags: Database
📋 This is my note-taking from what I learned in the class “Introduction To Database Concept”
Objectives
- Define database terms
- Identify the purpose of a database management system (DBMS)
- Explain database design using entity- relationship models and normalization
- Explain the purpose of a Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Understand how this textbook’s topics are sequenced and how the two sample databases are used
Database Terminology
- Database → logical structure to store data
- Database management system (DBMS) → software used to create and interact with the database
Database Components
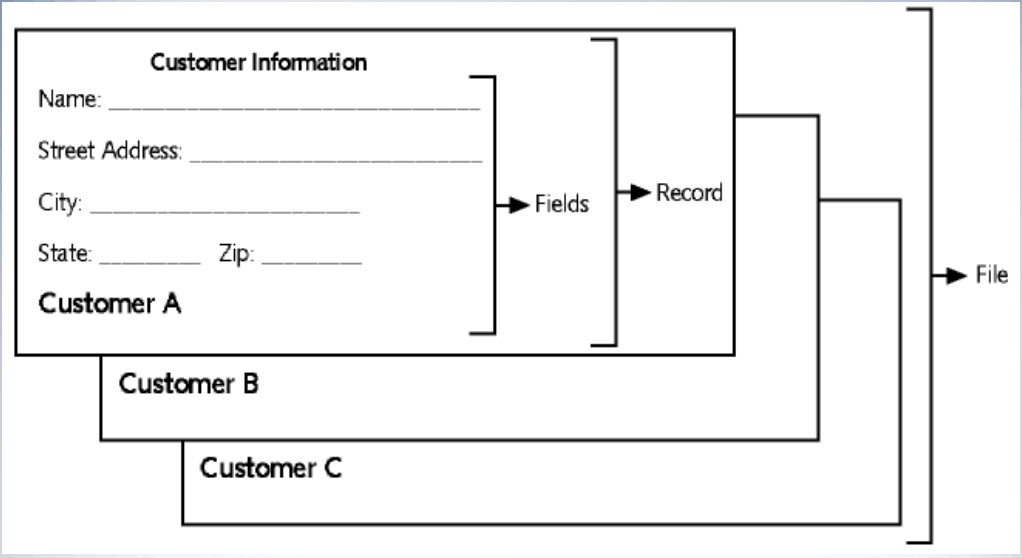
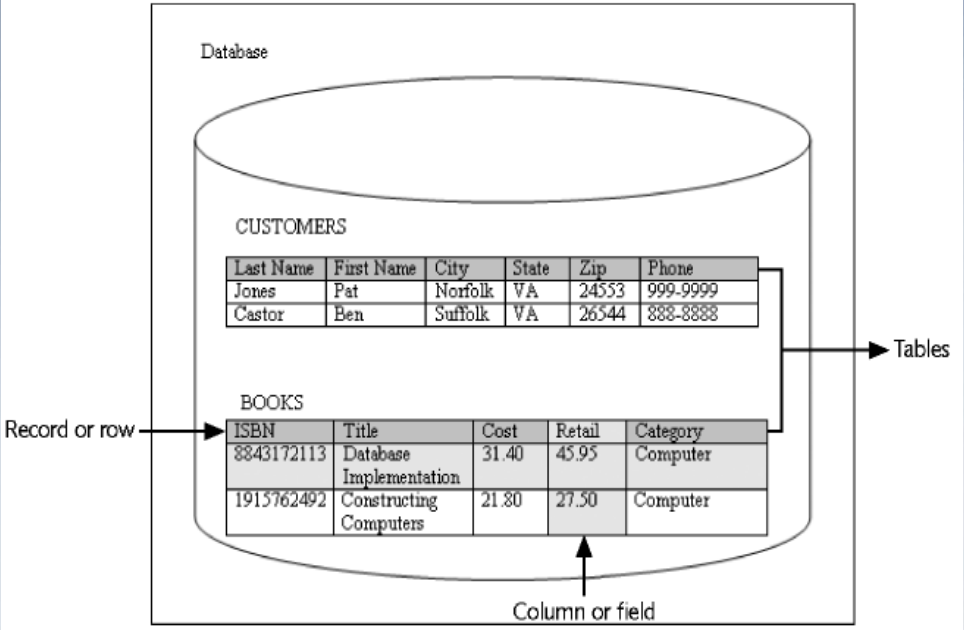
Character
- Basic unit of data
- Can be a letter, number, or special symbol
Field
- A group of related characters
- Represents an attribute or characteristic of an entity
- Corresponds to a column in the physical database
Record
- A collection of fields for one specific entity
- Corresponds to a row in the physical database
File
- A group of records about the same type of entity
Database Management System
- Data storage: manage the physical structure of the database
- Security: control user access and privileges
- Multi-user access: manage concurrent data access
- Backup: enable recovery options for database failures
- Data access language: provide a language that allows database access
- Data integrity: enable constraints or checks on data
- Data dictionary: maintain information about database structure
- Metadata: Data about data
Database Design
Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
- Systems investigation → understanding the problem
- Systems analysis → understanding the solution
- Systems design → creating the logical and physical components
- Systems implementation → placing completed system into operation
- Systems maintenance and review → evaluating the implemented system
Entity-Relationship Model (E-R Model)
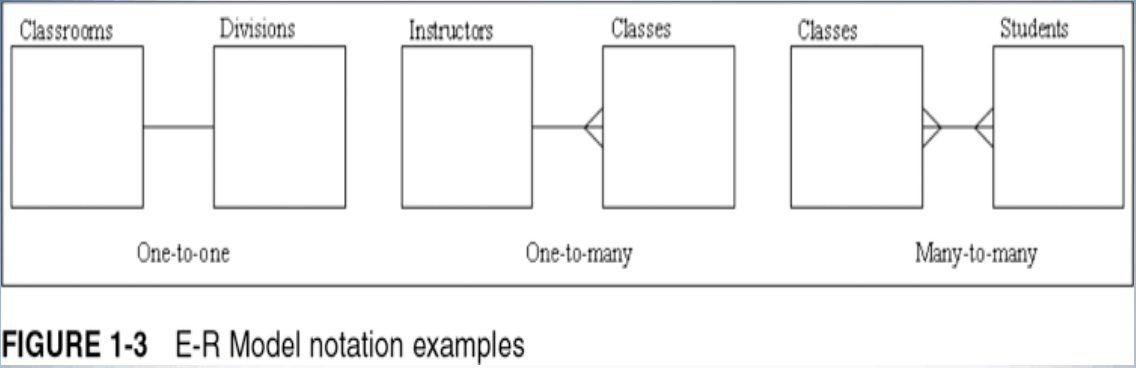
- Used to depict the relationship that exists among entities
-
- The following relationships can be included in an E-R model:
-
- One-to-one
-
- One-to-many
-
- Many-to-many
One-to-One Relationship:
- Each occurrence of data in one entity is represented by only one occurrence of data in the other entity
- Example: Each individual has just one Social Security number (SSN) and each SSN is assigned to just one person
One-to-Many Relationship:
- Each occurrence of data in one entity can be represented by many occurrences of the data in the other entity
- Example: A class has only one instructor, but each instructor can teach many classes
Many-to-Many Relationship:
- Data can have multiple occurrences in both entities
- Example: A student can take many classes, and each class is composed of many students
- Can not be included in the physical database
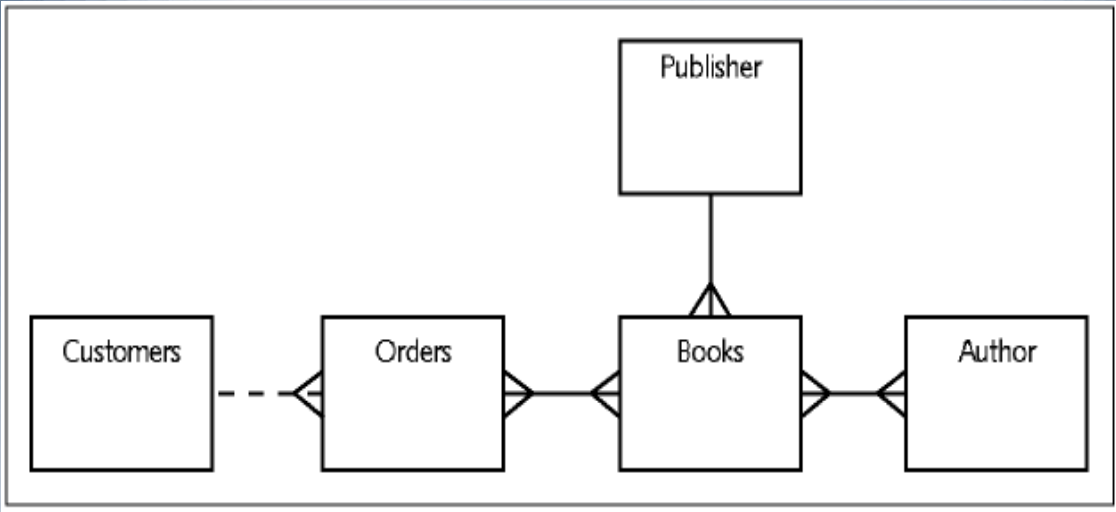
JustLee Example E-R Model:
Normalization
Database Normalization:
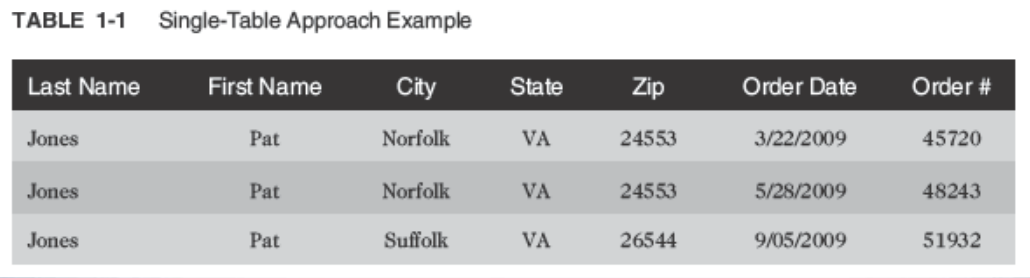
- Determines required tables and columns for each table
- Multi-step process
- Used to reduce or control data redundancy
- Data redundancy → refers to having the same data in different places within a database
- Data anomalies → refers to data inconsistencies
Unnormalized Data:
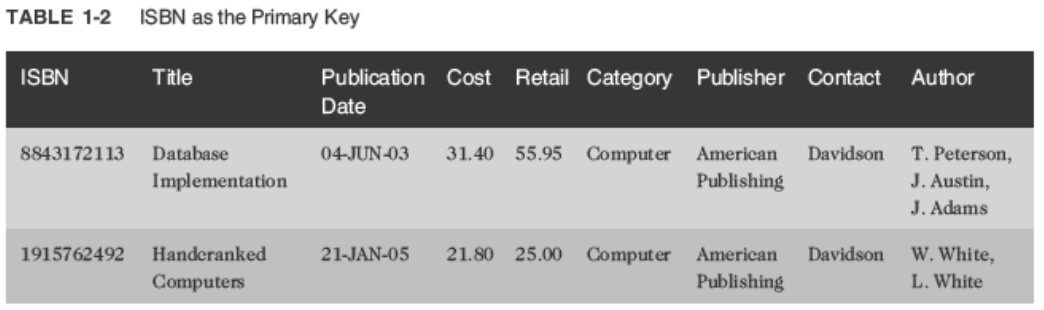
- Contains repeating groups in the Author column in the BOOKS table
First-Normal Form (1NF):
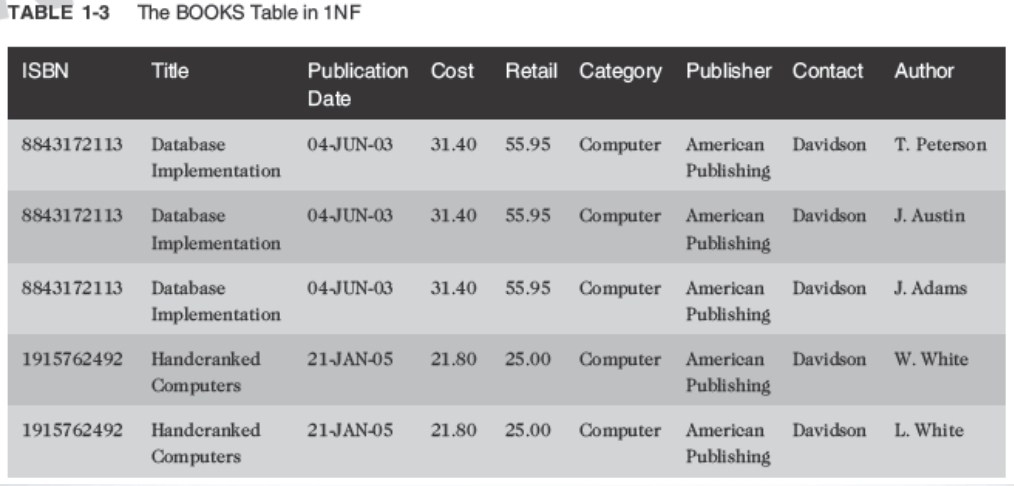
- Primary key is identified
- Repeating groups are eliminated
- ISBN and Author columns together create a composite primary key
Composite Primary Key:
- More than one column is required to uniquely identify a row
- Can lead to partial dependency → a column is only dependent on a portion of the primary key
Second-Normal Form (2NF):
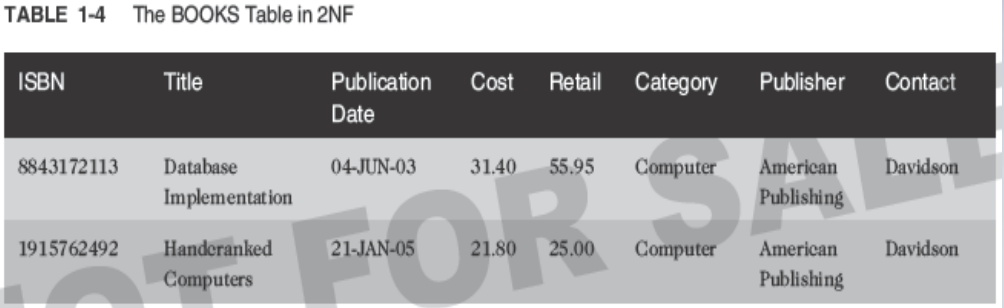
-
- Partial dependency must be eliminated
- Break the composite primary key into two parts, each part representing a separate table
- BOOKS table in 2NF
Third-Normal Form (3NF):
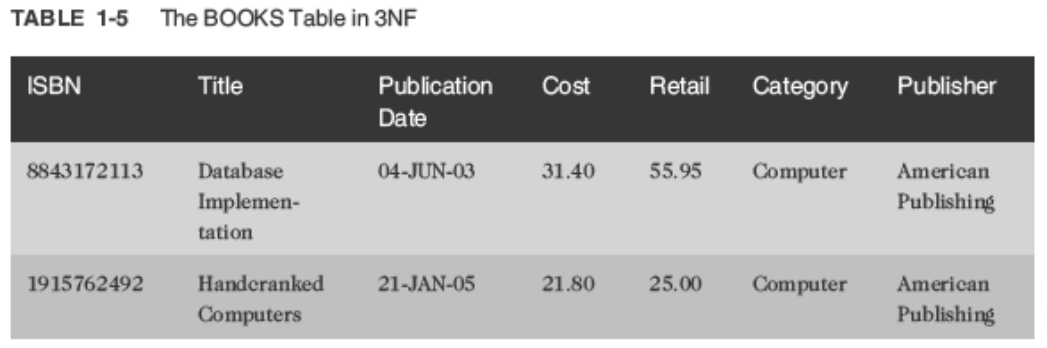
- Publisher contact name has been removed
Summary of Normalization Steps
- 1NF: eliminate repeating groups, identify the primary key
- 2NF: table is in 1NF, and partial dependencies are eliminated
- 3NF: table is in 2NF, and transitive dependencies are eliminated
Relating Tables within the Database
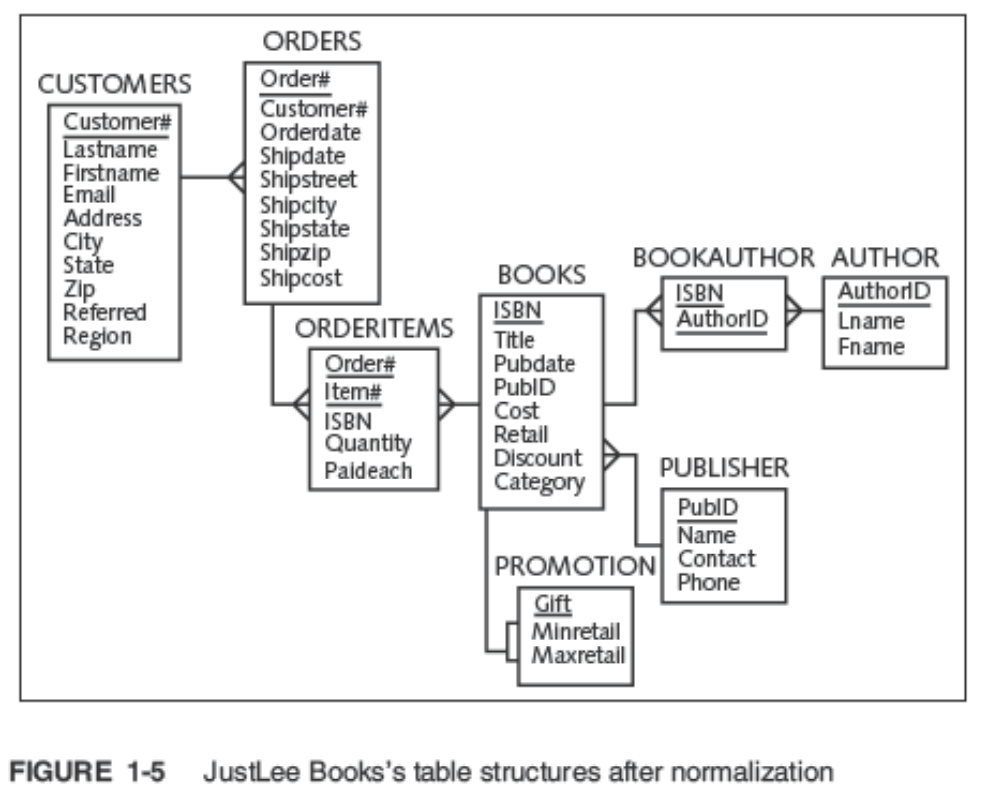
- Once tables are normalized, make certain tables are linked
- Tables are linked through a common field
- A common field is usually a primary key in one table and a foreign key in the other table
Lookup Table
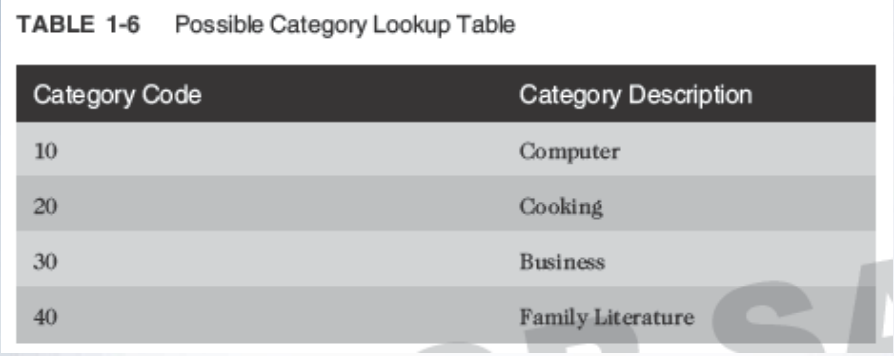
- Common reference for descriptive data tables referenced in a foreign key
Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Data sub-language
-
- Used to:
-
- Create or modify tables
-
- Add data to tables
-
- Edit data in tables
-
- Retrieve data from tables
- ANSI and ISO standards
Databases Used in this Textbook - JustLee Books Database
Assumptions:
- No back orders or partial shipments
- Only U.S. addresses
- Completed orders are transferred to the annual SALES table at the end of each month to enable faster processing on the ORDERS table
Topic Sequence
- The first half of the text will focus on creating a database
- The second half of the text will focus on querying or retrieving data from a database
Week 01 Demo
SELECT * FROM DUAL;
DESC DUAL;
--STUDENT TABLE CREATION
CREATE TABLE STUDENT
( SID NUMBER(6),
FNAME VARCHAR2(20),
LNAME VARCHAR2(20),
PRG VARCHAR2(5)
);
-- CHECK THE STRUCURE
SELECT * FROM STUDENT;
-- INSERT VALUES
INSERT INTO STUDENT VALUES (300123,'SHIRISH','BHUSAL','SET');
INSERT INTO STUDENT VALUES (300111,'SI','XU','SETAI');
INSERT INTO STUDENT VALUES (300222,'ASHISH','SHARMA','SET');
-- DELETE A TABLE
DROP TABLE STUDENT;
create table DEPARTMENTS (
deptno number,
name varchar2(50) not null,
location varchar2(50),
constraint pk_departments primary key (deptno)
);
DESC DEPARTMENTS;
SELECT * FROM STUDENT;
Summary
- A DBMS is used to create and maintain a database
- A database is composed of a group of interrelated tables
- A file is a group of related records; a file is also called a table in the physical database
- A record is a group of related fields regarding one specific entity; a record is also called a row
- A record is considered unnormalized if it contains repeating groups
- A record is in first-normal form (1NF) if no repeating groups exist and it has a primary key
- Second-normal form (2NF) is achieved if the record is in 1NF and has no partial dependencies
- After a record is in 2NF and all transitive dependencies have been removed, then it is in third-normal form (3NF), which is generally sufficient for most databases
- A primary key is used to uniquely identify each record
- A common field is used to join data contained in different tables
- A foreign key is a common field that exists between two tables but is also a primary key in one of the tables
- A lookup table is a common term for a table referenced in a foreign key
- A Structured Query Language (SQL) is a data sub-language that navigates the data stored within a database’s tables
C.1 Demo
-- Week 01 --
SELECT * FROM DUAL;
DESC DUAL;
-- CREATE 'STUDENT' TABLE
CREATE TABLE STUDENT
(
SID NUMBER(6),
FNAME VARCHAR2(20) NOT NULL,
LNAME VARCHAR2(20),
PRG VARCHAR2(5), --> PRG VARCHAR2(5) CONSTRAINT PK_STUDENT PRIMARY KEY -> NOT NULL VALUE: FNAME, PRG
CONSTRAINT PK_STUDENT PRIMARY KEY (SID) --> NOT NULL VALUE: SID, FNAME
);
SELECT * FROM STUDENT;
DESC STUDENT;
-- INSERT A VALUE
INSERT INTO STUDENT VALUES (300123,'SEYEON','JO','SET');
-- DELETE A TABLE
DROP TABLE STUDENT;

Leave a comment