[C#] C# Control Structure - Selection
Categories: CS
📋 This is my note-taking from what I learned in the class “Programming 1 - COMP 100-002”
The Control Structures

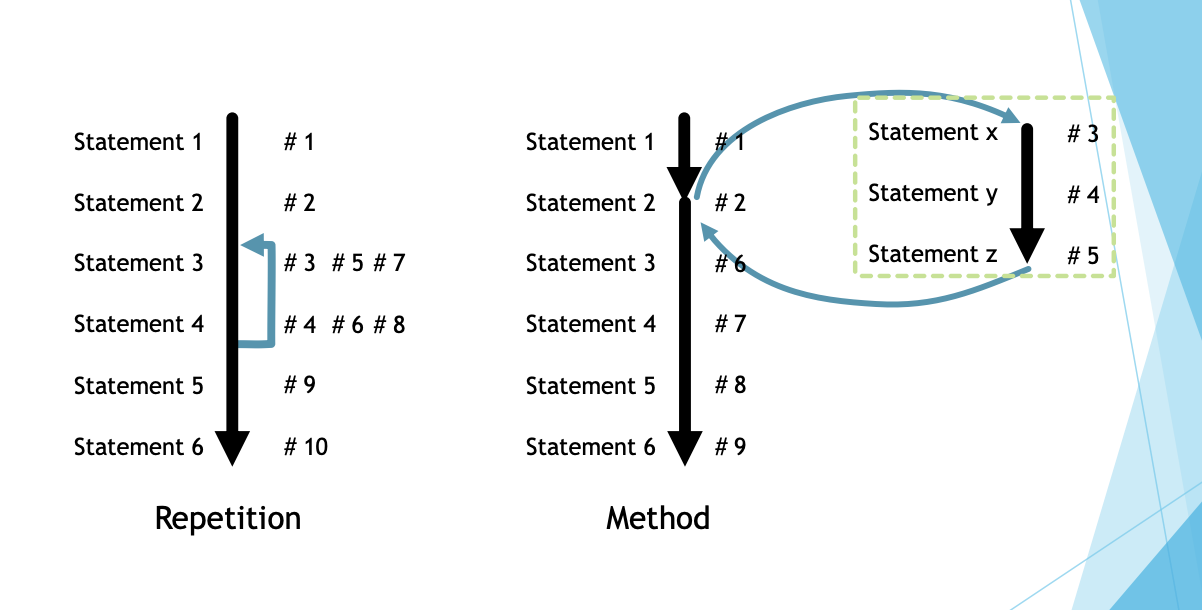
Control Structures: Conditional/Selection/Branching
- This structure facilitate selective execution of code.
- In some situation, the code block can be ignored or can be processed.
- In C#, this is done with the “if” and the “switch” statements.
- The latter is easier to understand but limited to test equality for ints, chars, and strings.
- This allow you to write any program that is can be programmed (i.e. computable)
- Also called branching or selection because control is divided.
if Statement
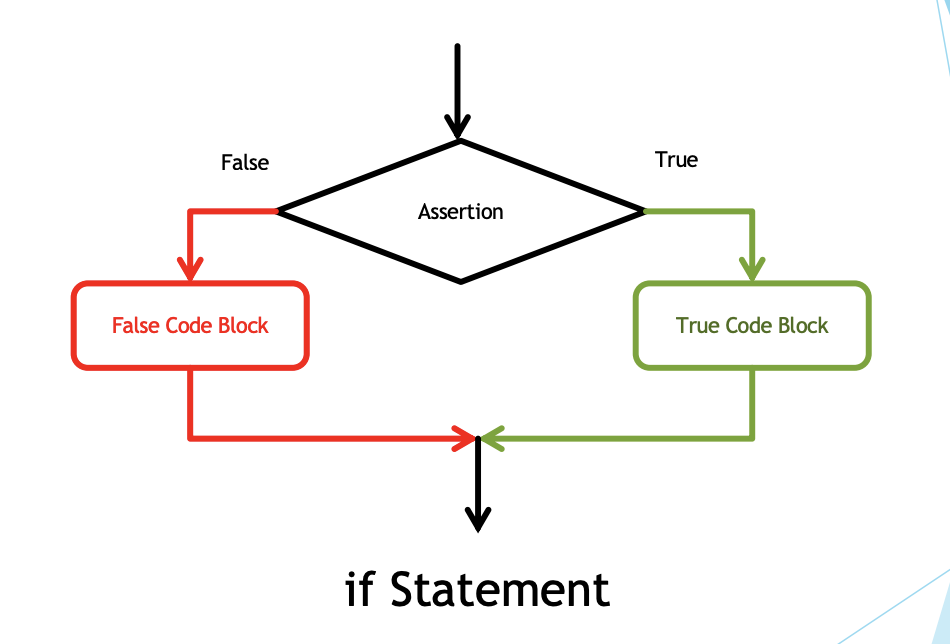
-
Uses assertions and code blocks.
-
Assertion is a Boolean expression.
- You may use the relational operators (==, !=, <, <=, >, >=) to build a Boolean expression.
-
A code block can be a single statement OR a set of statements enclosed within a pair of curly braces.
- In an if-statement, there are normally 2 blocks - true and false block.
Syntax
if (<<bool expression>>) { <<true block>> } else { <<false block>> }
if (weight > 100)
{
Console.WriteLine("Heavy");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Not heavy");
}
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.Write("Enter your age: ");
int age = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (age < 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Age cannot be negative");
}
}
}
Console.Write("Enter an integer: ");
int number = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (number % 2 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{number} is even");
}
else //you don’t need to check for odd. Why?
{
Console.WriteLine($"{number} is odd");
}
Console.Write("Are you married (True/False)?: ");
bool isMarried = Convert.ToBoolean(Console.ReadLine());
if (isMarried) //the value in the assertion is already bool
{
Console.WriteLine("Sorry this is a singles only club.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Welcome.");
}
Tips
-
Always use a pair of braces to enclosed your true code block or your false code block.
-
Use positive logic.
- if(a == b) // positive logic
- if(!a == b) // negative logic
-
The selection statement is best described using a Flowchart.
Note this!
- The Selection Control Structures adds immense power to the language.
- Selection statements can be nested to do almost everything.
- Another selection statement is the switch-statement.

Leave a comment