[Ad-Oracle-Sql] 5. Basic PL/SQL & Block Structures
Categories: Ad-Oracle-Sql
📋 This is my note-taking from what I learned in the class “Advanced Database Concepts”
Objective
- Programming fundamentals
- PL/SQL blocks
- How to define and declare variables
- How to initialize and manage variable values
- The NOT NULL and CONSTANT variable options
- How to perform calculations with variables
- The use of SQL single-row functions in PL/SQL statements
- Decision structures: IF-THEN and CASE
- Looping actions: basic, FOR and WHILE
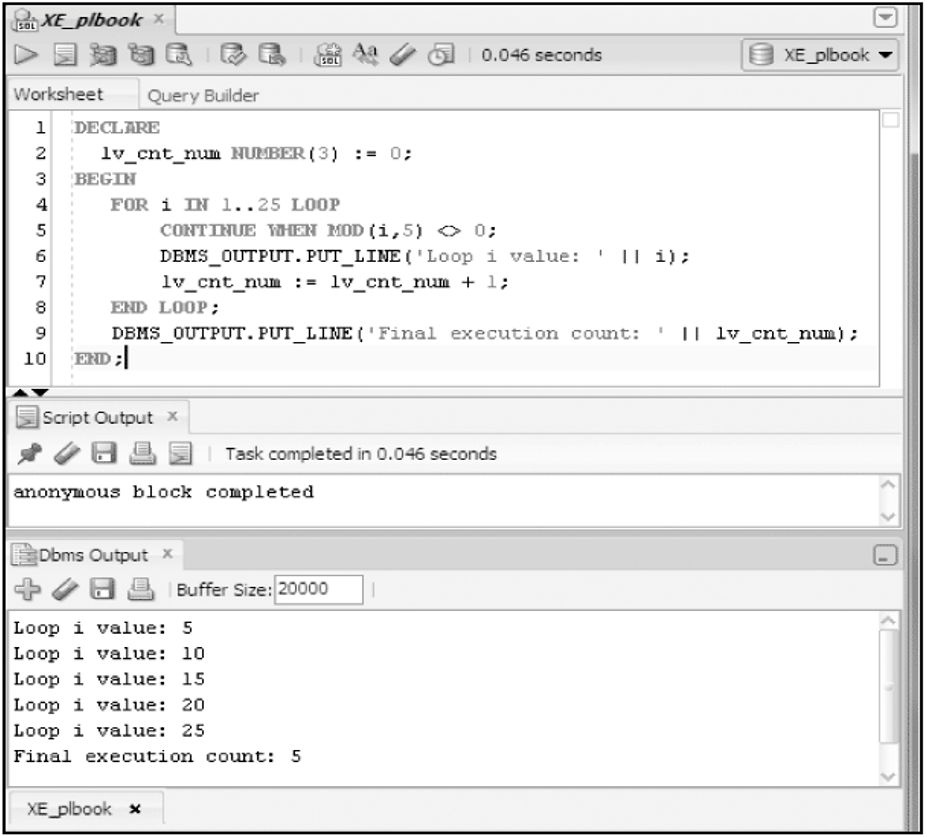
- CONTINUE statements
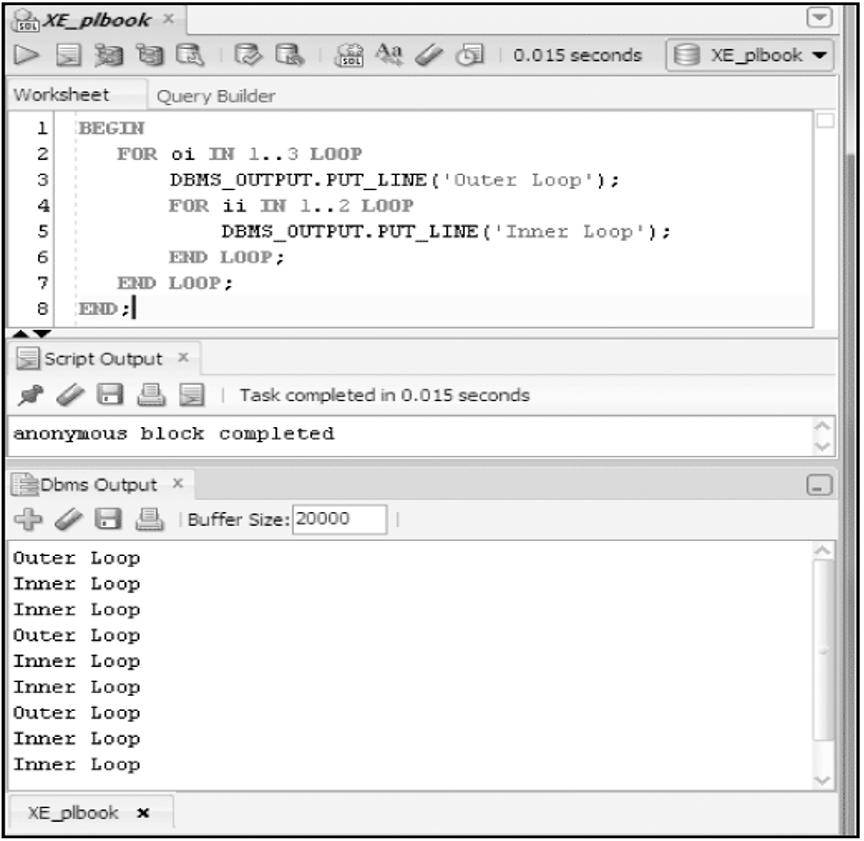
- Nested Statements
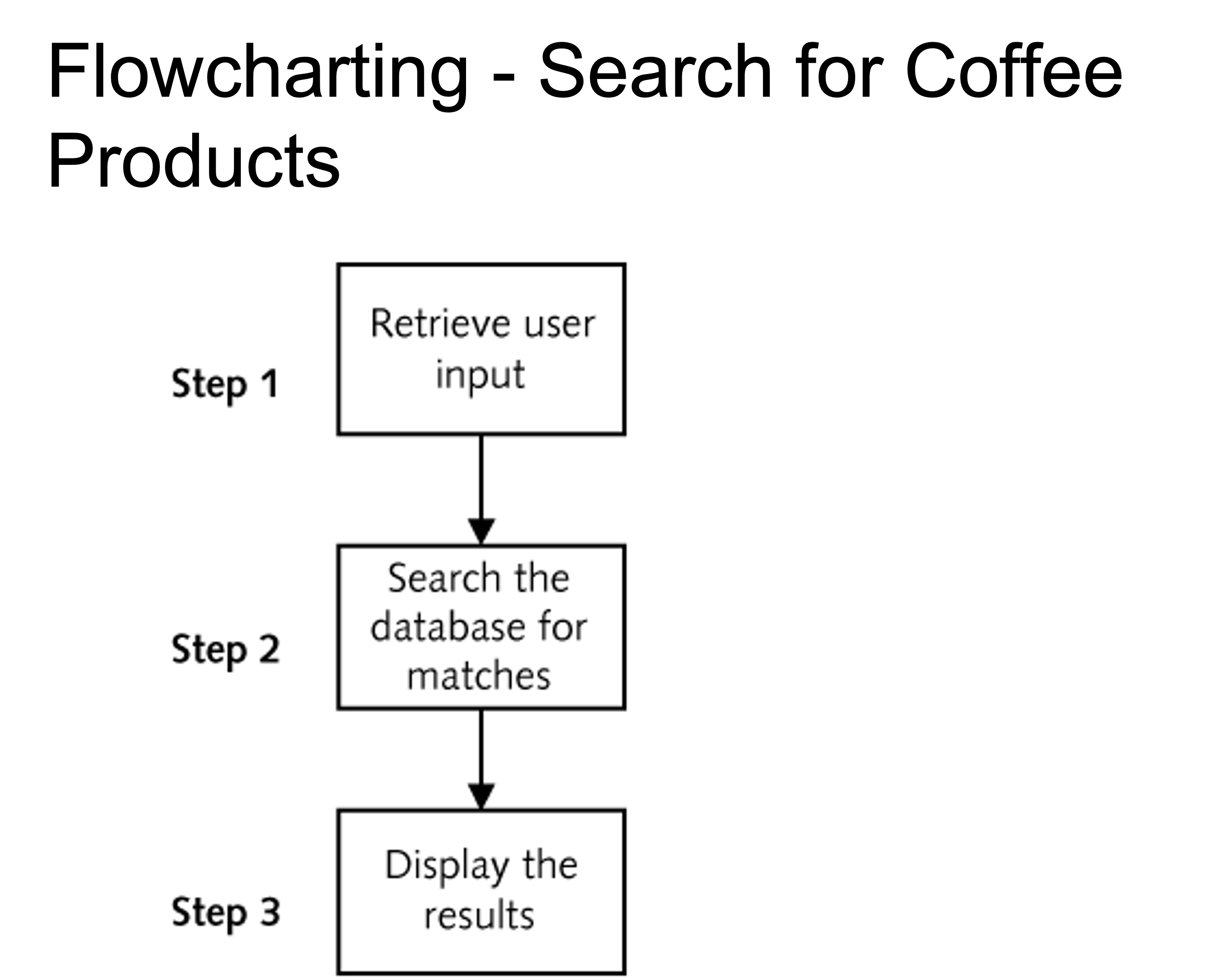
Program Logic Flow
- Identify sequence of actions needed prior to coding
- Use a flowchart to visually represent the sequence of actions
Flowcharting - Search for Coffee Products
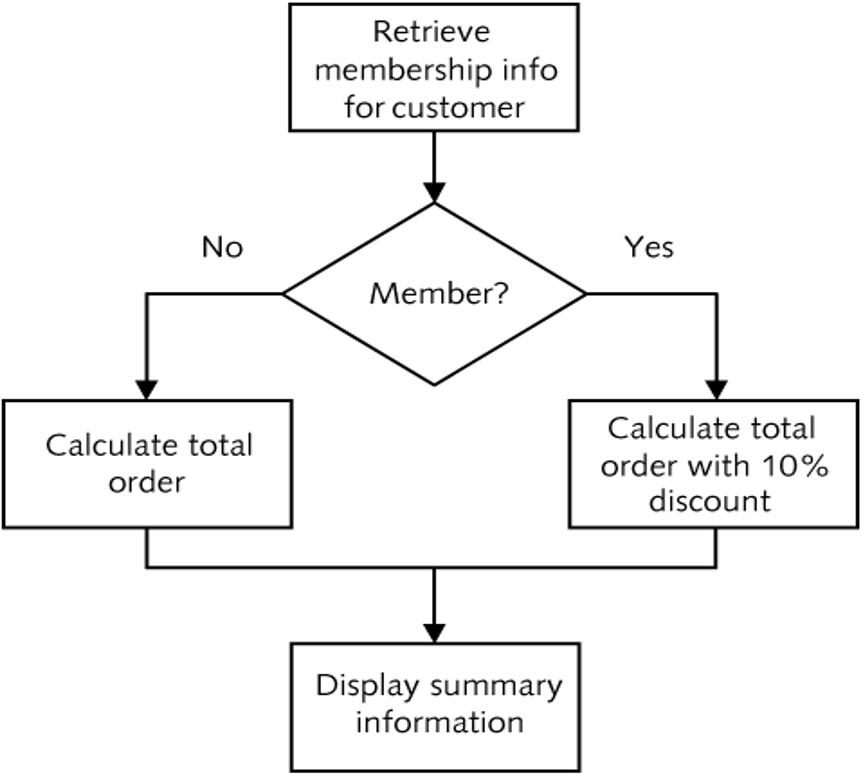
Decision Structures
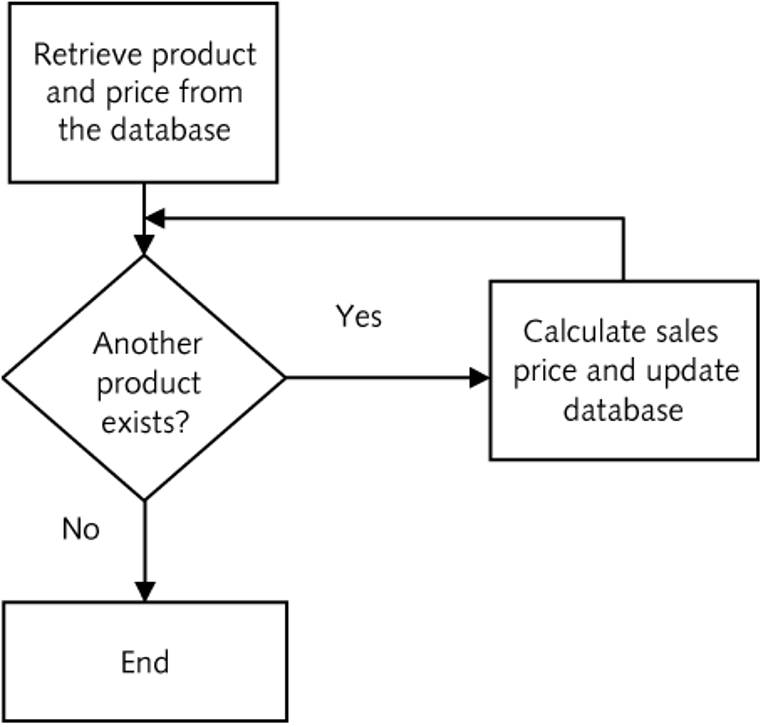
Looping Structures
PL/SQL Block Questions
- What is a block?
- What are the different segments of a block?
- How does data get into a block?
- How are different data types handled?
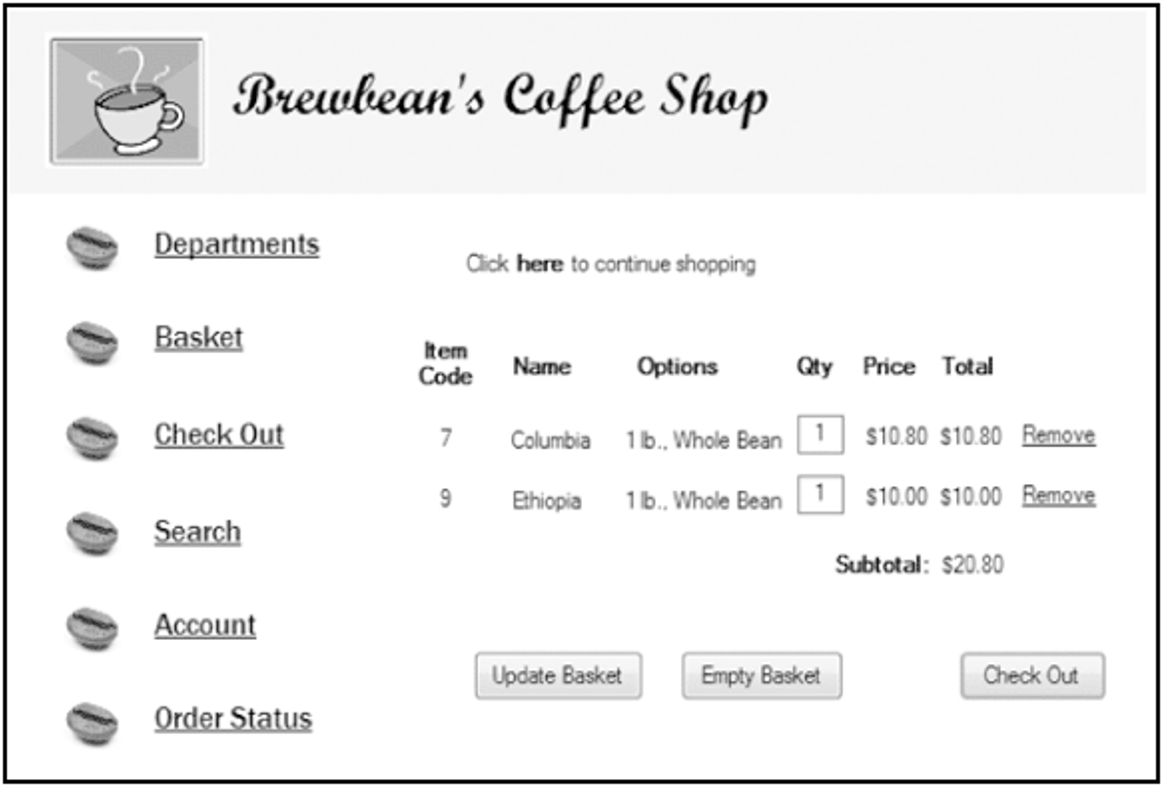
Brewbean’s Challenge
PL/SQL Block Structure
- DECLARE – create variables, cursors, and types
- BEGIN – SQL, logic, loops, assignment statements
- EXCEPTION – error handling
- END – close the block
Variable Names
- Begin with alpha character
- Up to 30 characters
- Can contain upper and lowercase letters, numbers,
_,$,#
Scalar Variable Data Types
-
- Character
-
- CHAR(n)
-
- VARCHAR2(n)
-
- Numeric
-
- NUMBER(p,s)
-
- Date
-
- DATE
-
- Boolean
-
- BOOLEAN
Note: Only holds a single value
Example Scalar Declarations
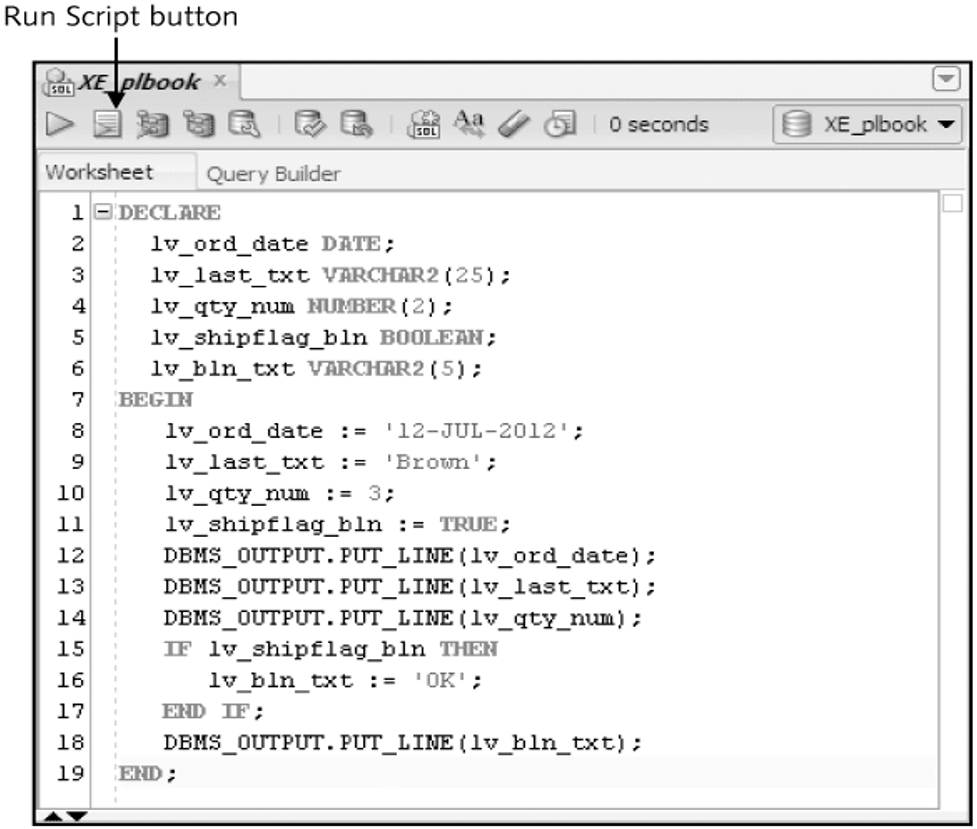
DECLARE
lv_ord_date DATE;
lv_last_txt VARCHAR2(25);
lv_qty_num NUMBER(2);
lv_shipflag_bln BOOLEAN;
BEGIN
---- PL/SQL executable statements ----
END;
Note: Minimum requirements are variable name and data type
Test Variables
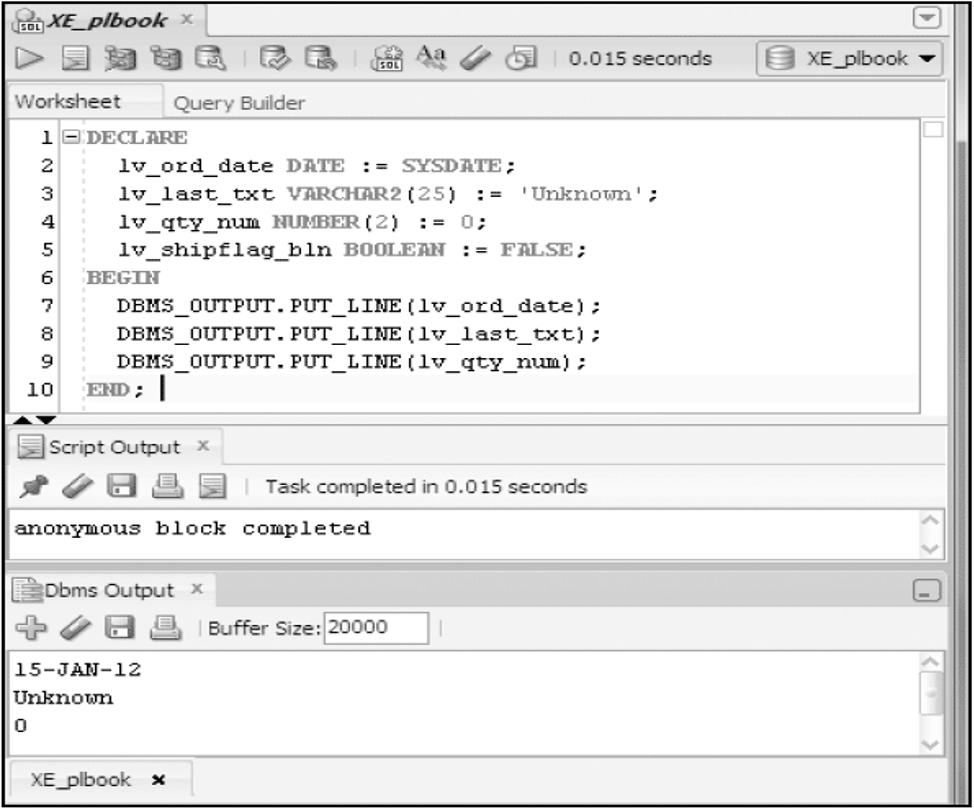
Variable Initialization
- Set a variable value when the variable is created
DECLARE
lv_ord_date DATE := SYSDATE;
lv_last_txt VARCHAR2(25) := 'Unknown';
lv_qty_num NUMBER(2) := 0;
lv_shipflag_bln BOOLEAN := FALSE;
BEGIN
---- PL/SQL executable statements ----
END;
Test Variable Initialization
Variable Declaration Options
- NOT NULL – the variable must always contain a value
- CONSTANT – the variable value can not be changed in the block
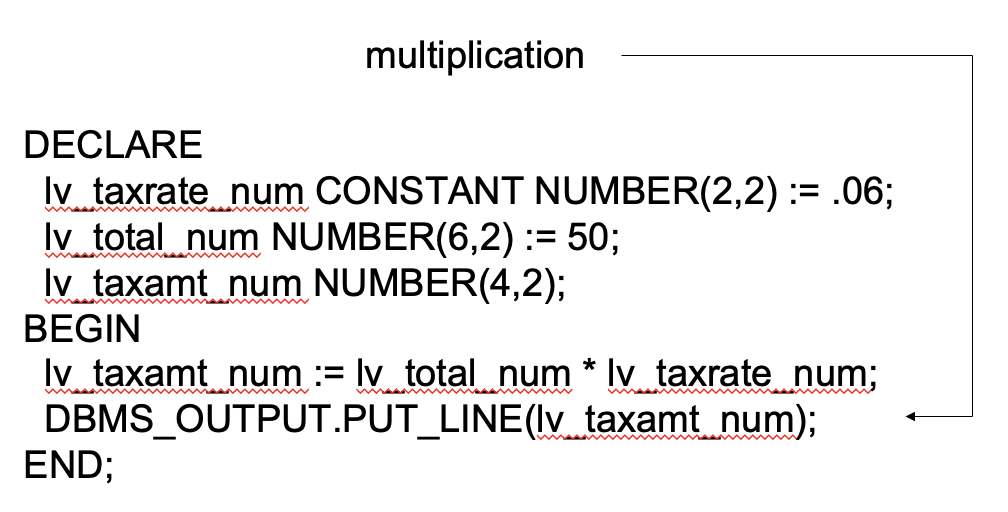
DECLARE
lv_shipcntry_txt VARCHAR2(15) NOT NULL := 'US';
lv_taxrate_num CONSTANT NUMBER(2,2) := .06;
BEGIN
---- PL/SQL executable statements ----
END;
Calculations with Scalar Variables
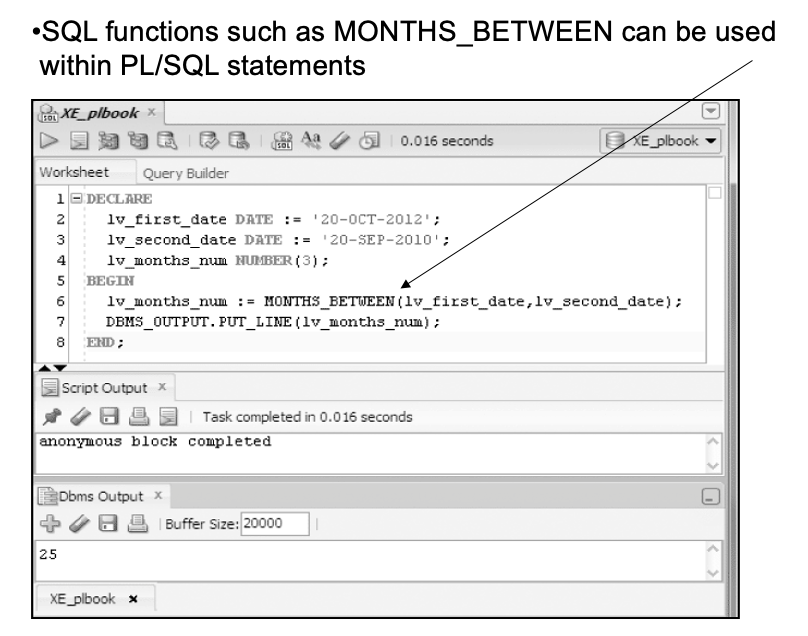
Using SQL Functions
Decision Structures
- Control which statements in a PL/SQL block will execute
- Enables conditions to be tested to determine the flow of statement execution
- Most programming languages provide IF and CASE statements to enable conditional processing
-
- IF Statements
-
- Simple IF
-
- IF/THEN/ELSE
-
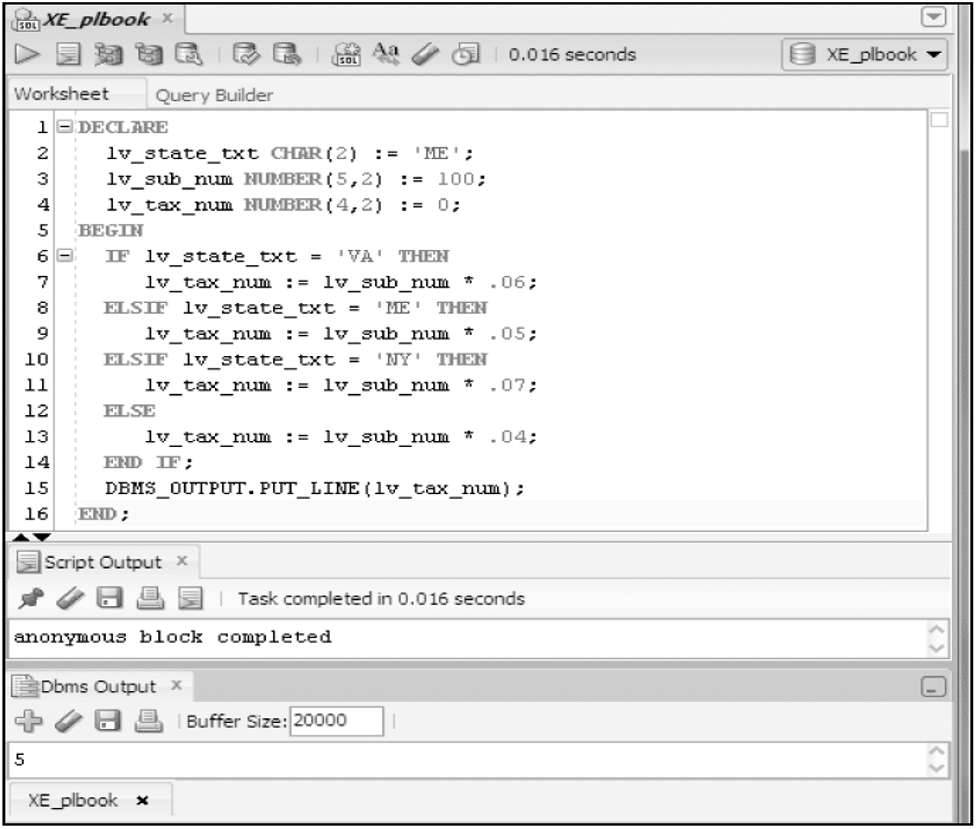
- IF/THEN/ELSIF/ELSE
-
- CASE Statements
-
- Basic CASE statement
-
- Searched CASE statement
-
- CASE expression
Basic IF Statement
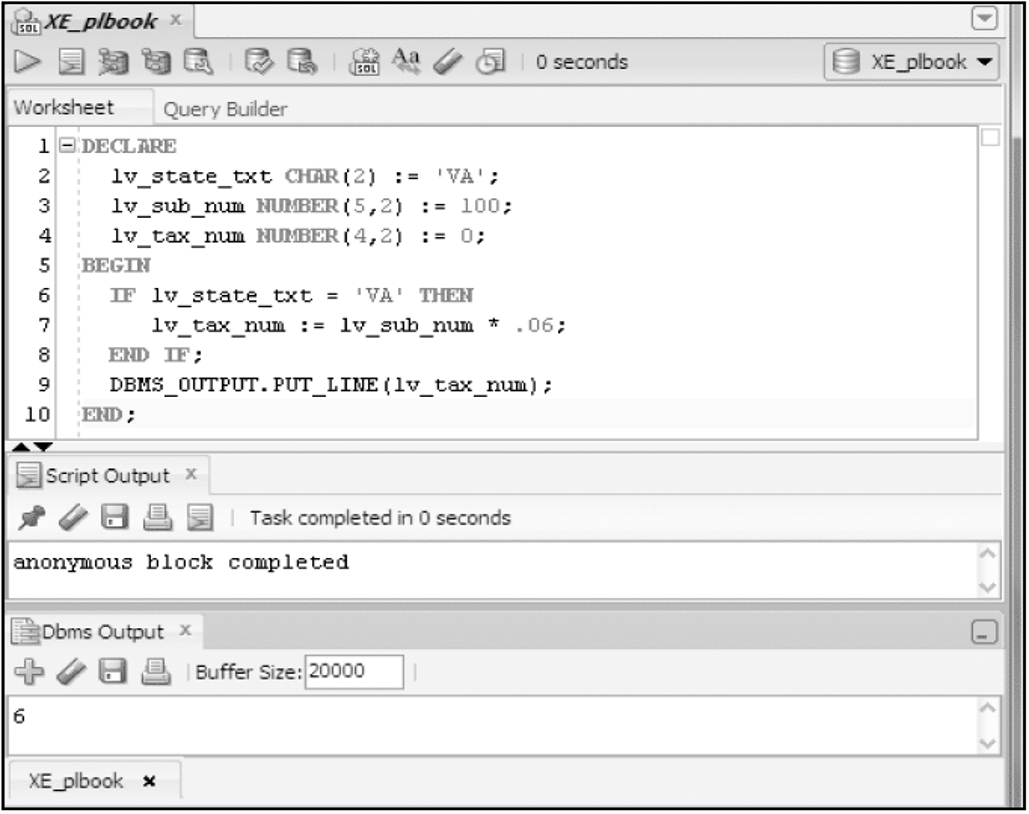
IF/THEN/ELSE
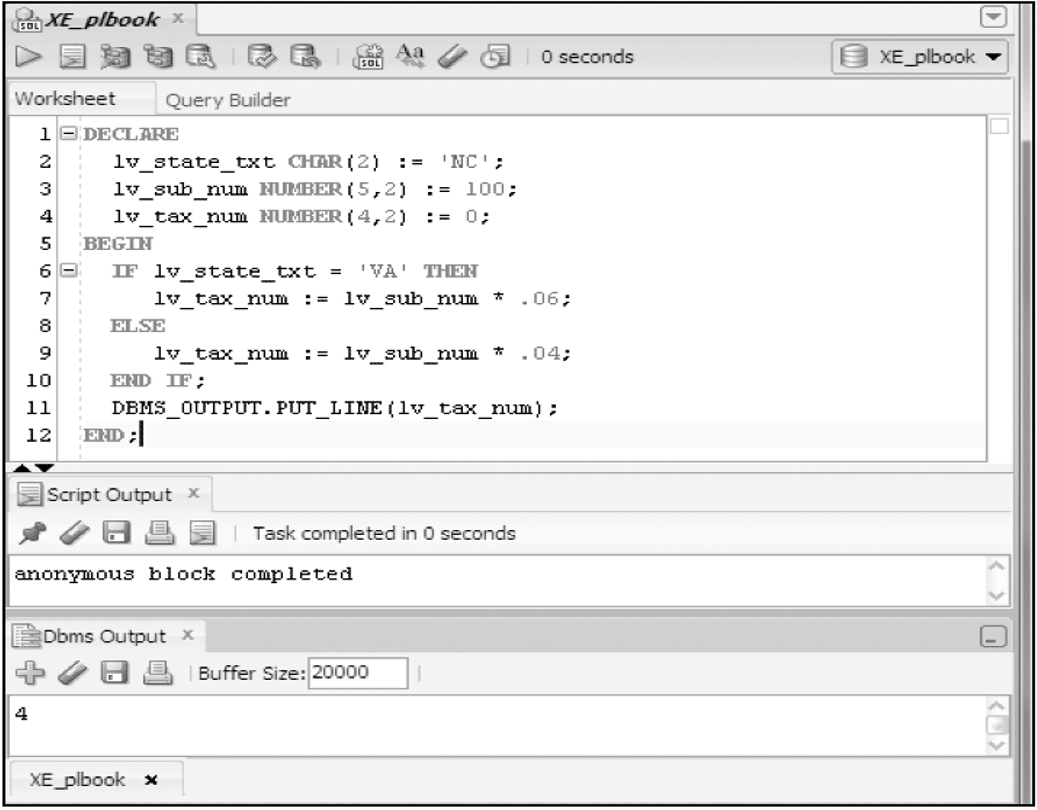
IF/THEN/ELSIF/ELSE
Nested IF
IF lv_type_txt = 'E' THEN
IF lv_price_num > 85 THEN # Inner or nested IF begins
lv_disc_num = .20;
ELSIF lv_price_num > 45 THEN
lv_disc_num = .15;
ELSE
lv_disc_num = .10;
END IF; # Inner or nested IF ends
ELSIF lv_type_txt = 'C' THEN
lv_disc_num = .05;
END IF;
Logical Operators within IF
Logical operators (AND, OR) enable multiple conditions to be checked
IF lv_state_txt = 'VA' OR lv_state_txt = 'PA' THEN
lv_tax_num := lv_sub_num * .06;
ELSE
lv_tax_num := lv_sub_num * .04;
END IF;
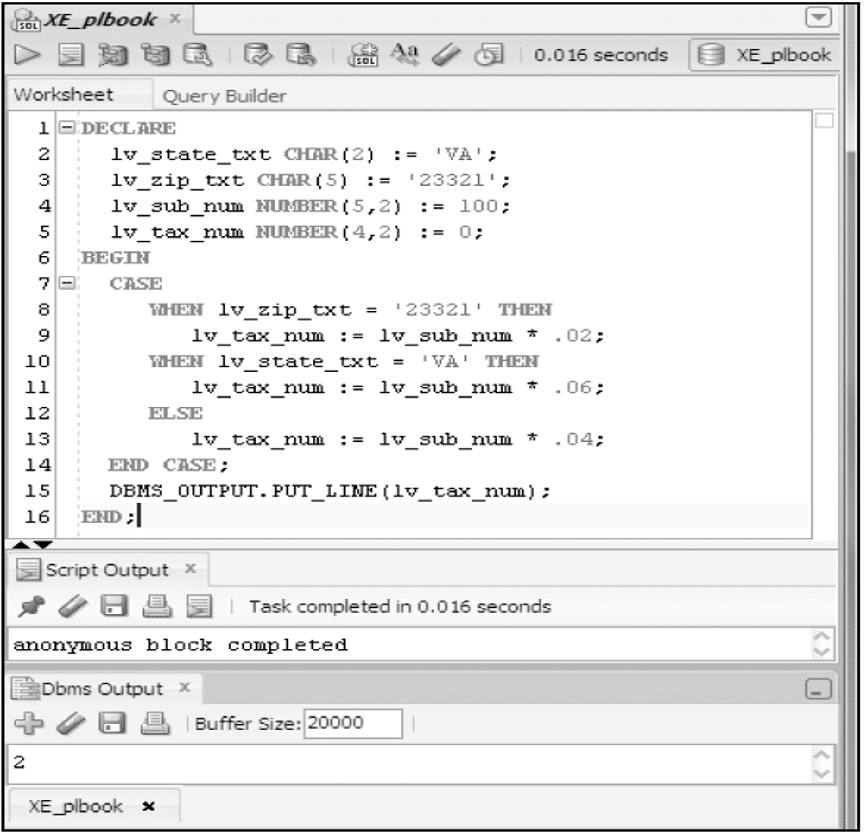
Basic CASE Statement
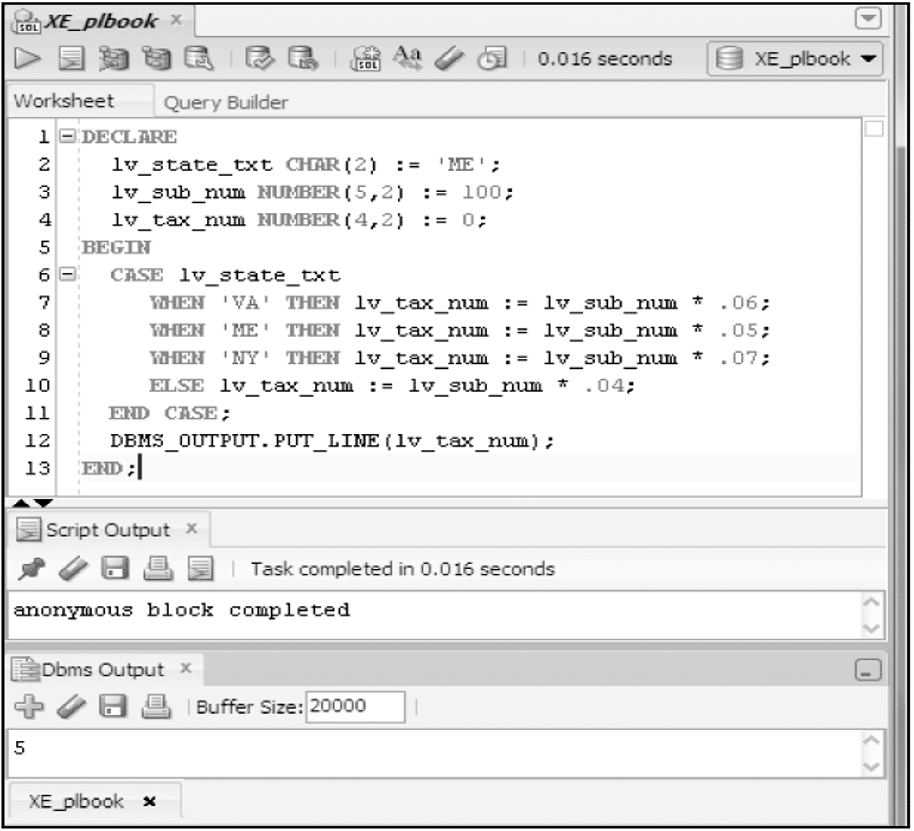
Searched CASE
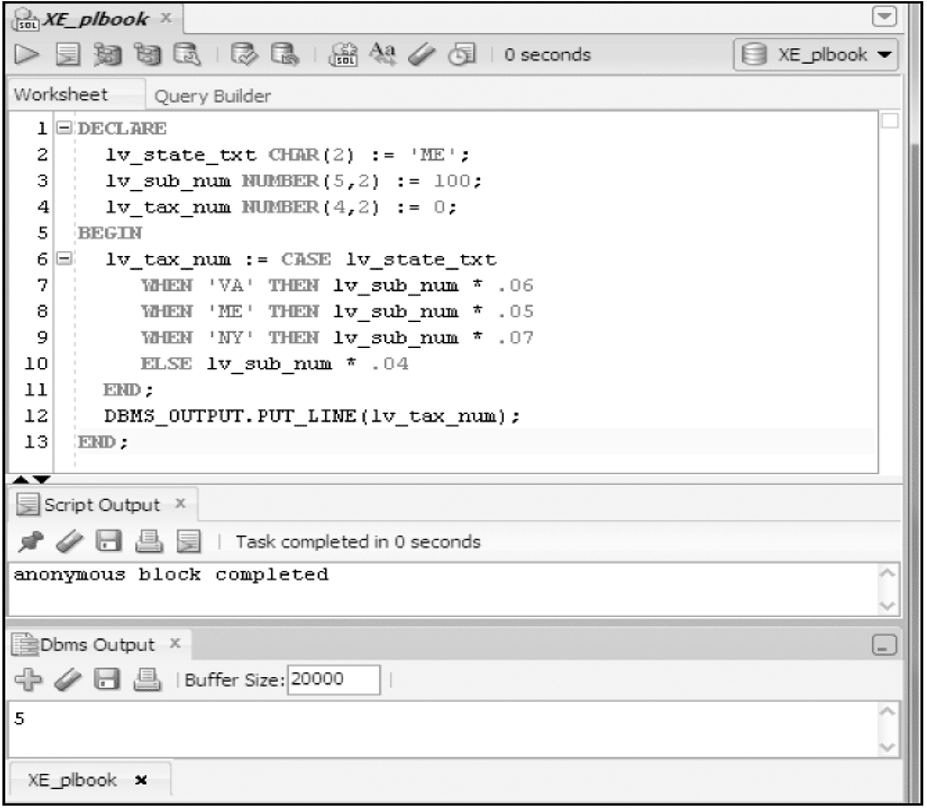
CASE Expression
Looping
- Enables a statement or set of statements to be executed more than once
- A loop must provide instructions of when to end the looping, or an ‘infinite’ loop will be produced
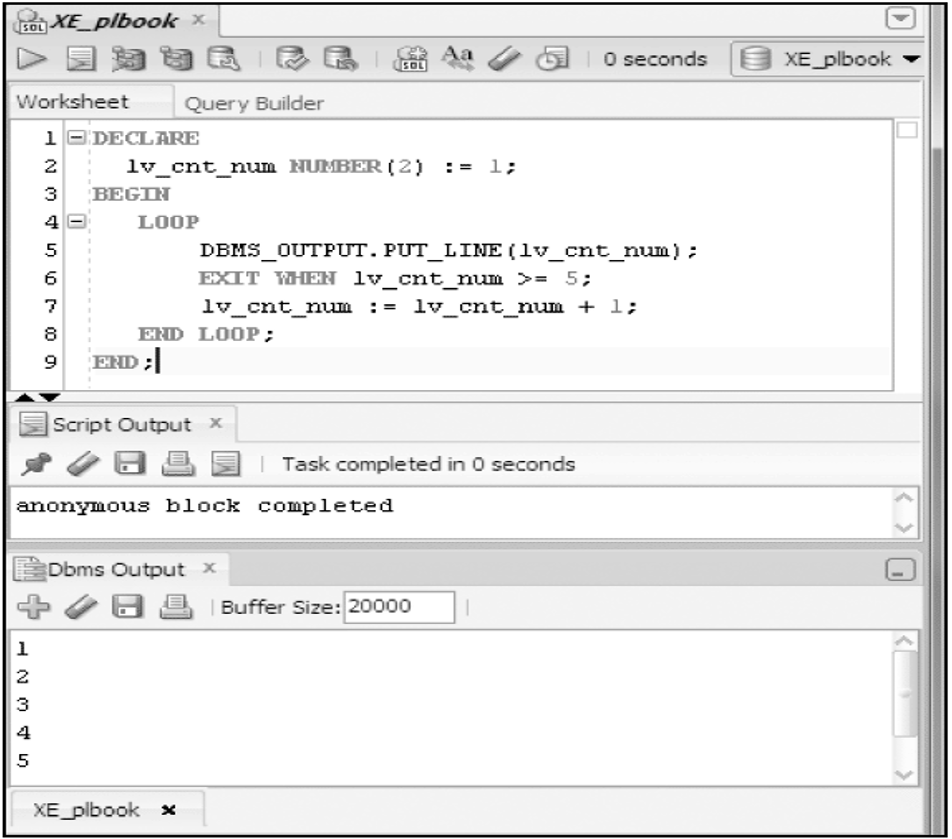
Basic LOOP
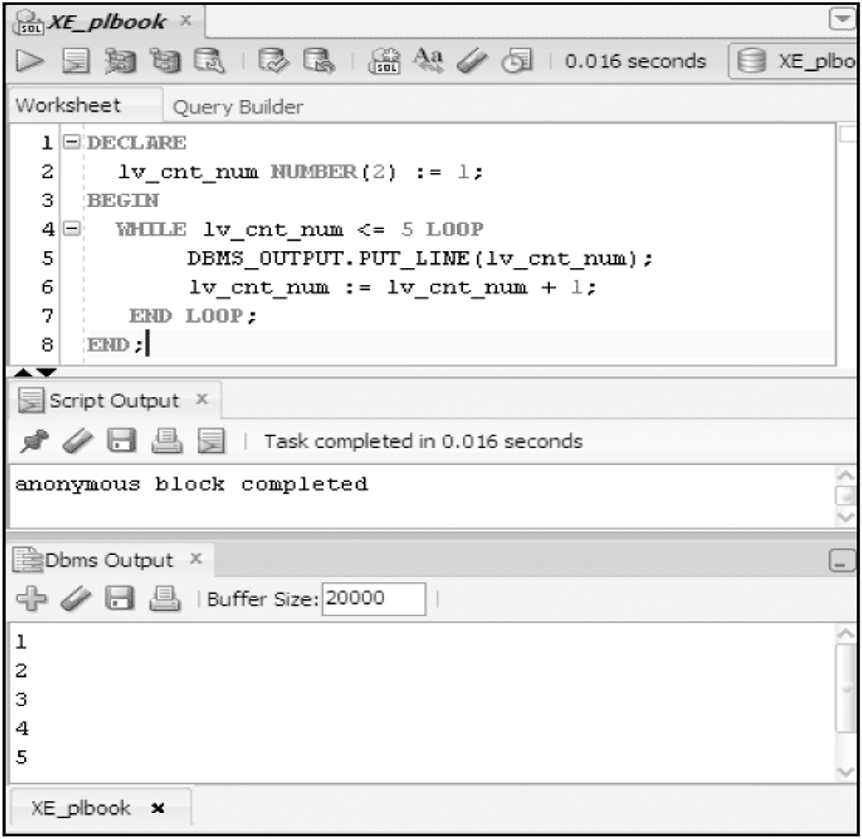
WHILE Loop
FOR Loop
CONTINUE Statement
Nested Loops
Summary
- A flowchart assists in laying out processing logic
- A PL/SQL block contains a DECLARE, BEGIN, EXCEPTION, and END sections
- Variables to hold values are declared
- Scalar variables hold a single data value
- Scalar variables can hold string values, numbers, dates, and - Boolean values
- DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE is used to display values
- IF statement structure is IF/THEN/ELSIF/ELSE
- CASE statements provide decision processing similar to IF statements
- Looping structures include: basic, WHILE, and FOR
- Host or bind variables can be used to interact with the application environment

Leave a comment