[Ad-Oracle-Sql] 2. Views
Categories: Ad-Oracle-Sql
Tags: Views
📋 This is my note-taking from what I learned in the class “Advanced Database Concepts”
Objective
- Create a view by using CREATE VIEW command or the CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW command
- Employ the FORCE and NOFORCE options
- State the purpose of the WITH CHECK OPTION constraint
- Explain the effect of the WITH READ ONLY option
- Update a record in a simple view
- Re-create a view
- Explain the implication of an expression in a view for DML operations
- Update a record in a complex view
- Identify problems associated with adding records to a complex view
- Identify the key-preserved table underlying a complex view
- Drop a view
- Explain inline views and the use of ROWNUM to perform a “TOP-N” analysis
- Create a materialized view to replicate data
Views
- Permanent objects that store no data
- Store a query
-
- Two purposes
-
- Reduce complex query requirements
-
- Restrict users’ access to sensitive data
Types of Views
-
- Simple view
- A view based upon a sub-query that only references one table and does not include any group functions, expressions, or a
GROUP BYclause
-
- Complex view
- A view based upon a sub-query that retrieves or derives data from one or more tables - and may also contain functions or grouped data
-
- Inline view
- A sub-query used in the
FROMclause of aSELECTstatement to create a “temporary” table that can be referenced by theSELECTandWHEREclauses of the outer statement
-
- Materialized view
- A view that replicates data by physically storing the results of the view query
Creating a View
- You use the
CREATE VIEWkeywords to create a view - Use
OR REPLACEif the view already exists - Use
FORCEif the underlying table does not exist at the time of creation - Provide new column names if necessary
CREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE|NOFORCE] VIEW
viewname (columnname, ...)
AS SELECT statement
[WITH CHECK OPTION [CONSTRAINT constraintname]]
[WITH READ ONLY];
WITH CHECK OPTIONconstraint - if used, prevents data changes that will make the data subsequently inaccessible to the viewWITH READ ONLY- prevents DML operations
Creating a Simple View
- Only references one table - no group functions,
GROUP BYclause, or expressions
CREATE VIEW inventory
AS SELECT isbn, title, retail_price
FROM books
WITH READ ONLY;
DML Operations on a Simple View
- Any DML operations are allowed through simple views unless created with
WITH READ ONLYoption - DML operations that violate constraints on the underlying table are not allowed
Creating a Complex View
- A complex view may contain data from multiple tables or data created with the
GROUP BYclause, functions, or expressions - Type of DML operations allowed depends on various factors
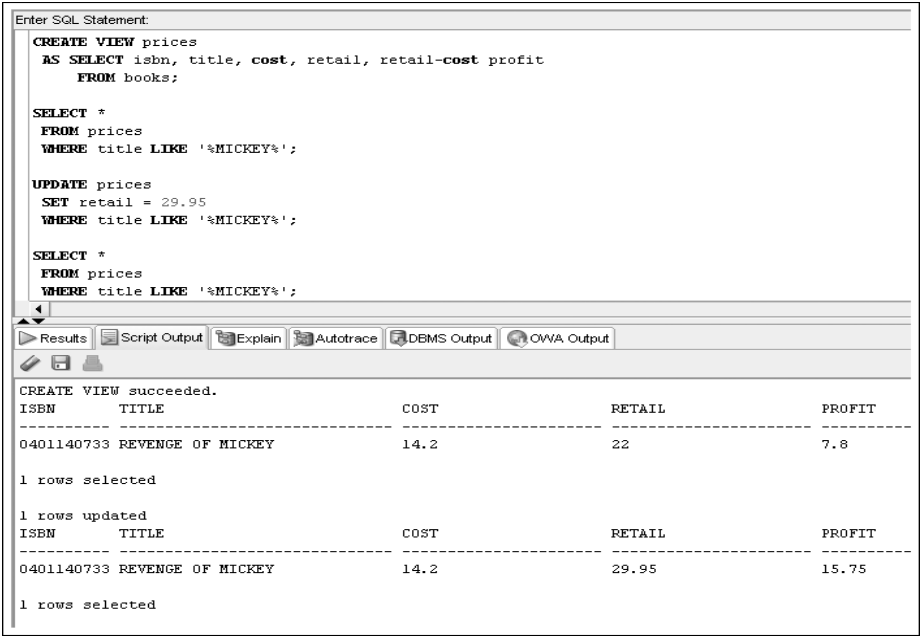
CREATE VIEW prices
AS SELECT isbn, title, cost, retail, retail-cost profit
FROM books;
DML Operations on a Complex View with an Arithmetic Expression
DML Operations on a Complex View Containing Data from Multiple Tables
- DML Operations cannot be performed on non-key-preserved tables, but they are permitted on key-preserved tables
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW prices
AS SELECT isbn, title, cost, retail, retail-cost profit, name
FROM books JOIN publisher USING(pubid);
-- CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW succeeded.
UPDATE prices
SET name = 'PRINT IS US'
WHERE title LIKE '%BEAR%';
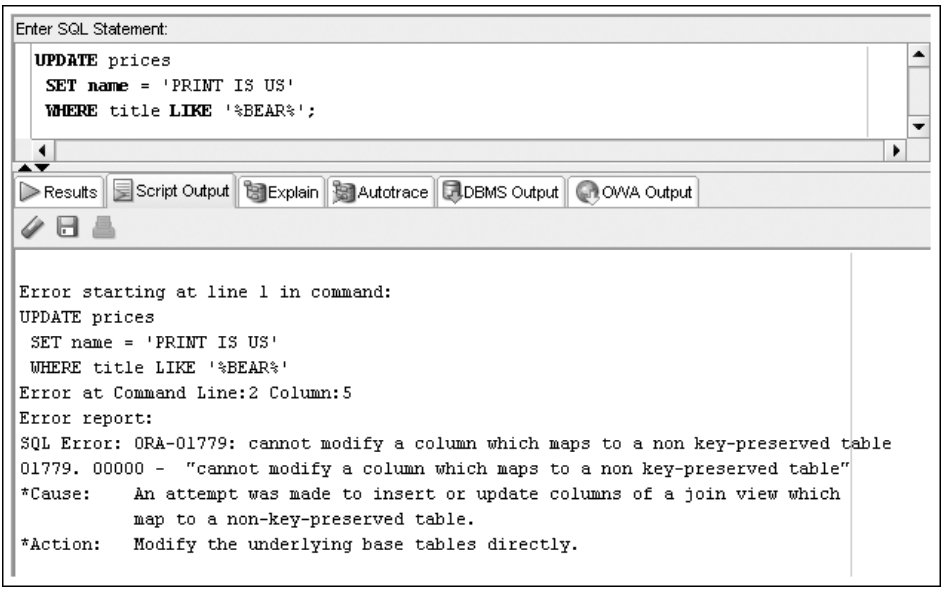
DML Operations on a Complex View Containing Functions or Grouped Data
- DML operations are not permitted if the view includes a group function or a
GROUP BYclause
CREATE VIEW balancedue
AS SELECT customer#, order#, SUM(quantity*retail) AS Amtdue
FROM customers
JOIN orders USING(customer#)
JOIN orderitems USING(order#)
JOIN books USING(isbn)
GROUP BY customer#, order#;
DELETE FROM balancedue
WHERE customer# = 1010;
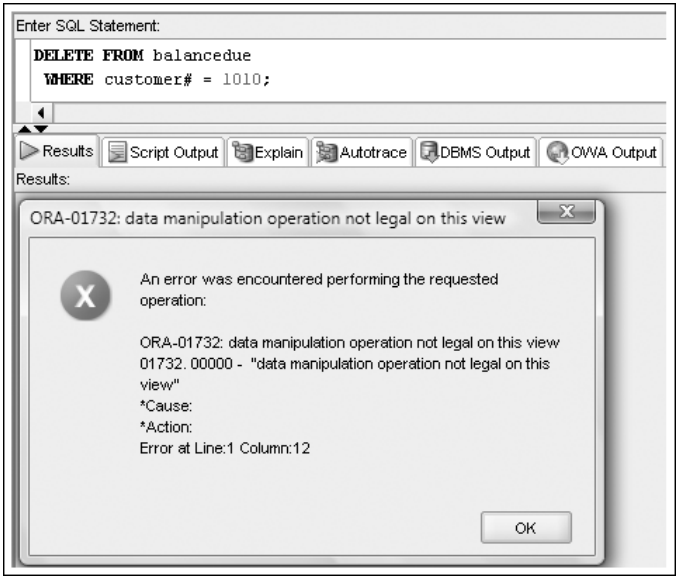
DML Operations on a Complex View Containing DISTINCT or ROWNUM
- DML operations on a view that contains the
DISTINCTkeyword orROWNUMare not permitted
Dropping a View
- Use
DROP VIEWcommand
DROP VIEW prices;
-- DROP VIEW prices succeeded.
Creating an Inline View
- An inline view is a temporary table created by using a sub-query in the
FROMclause - It can only be referenced while the command is being executed
- Most common usage -
TOP-Nanalysis
TOP-N Analysis
-
ORDER BYincluded to identify top values:-
- Describing for highest values
-
- Ascending for lowest values
- Extract data based on
ROWNUM
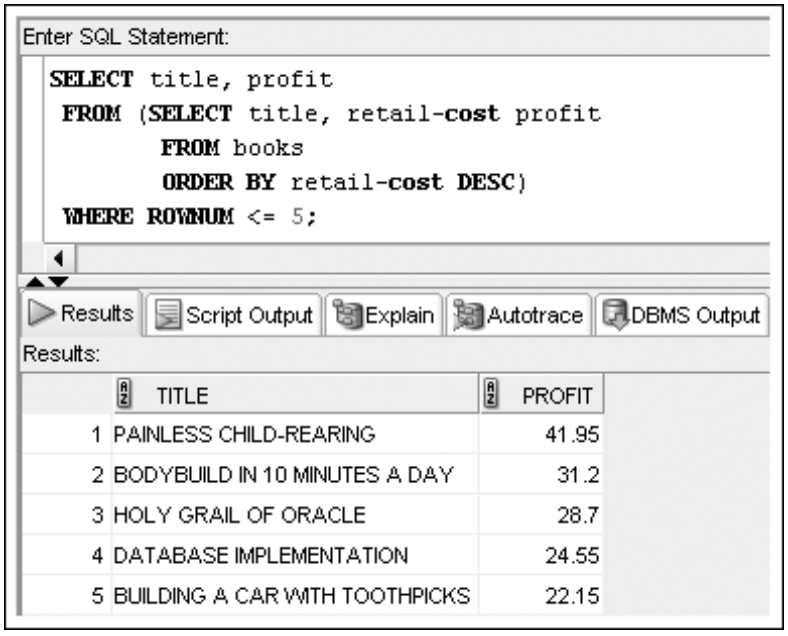
SELECT title, profit
FROM (SELECT title, retail-cost profit
FROM books
ORDER BY retail-cost DESC)
WHERE ROWNUM <= 5;
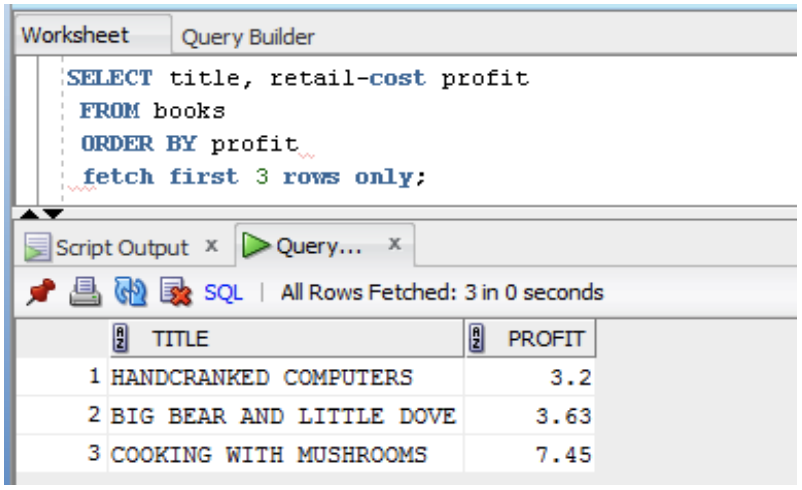
- Oracle 12c introduces a new row limiting clause (# rows)
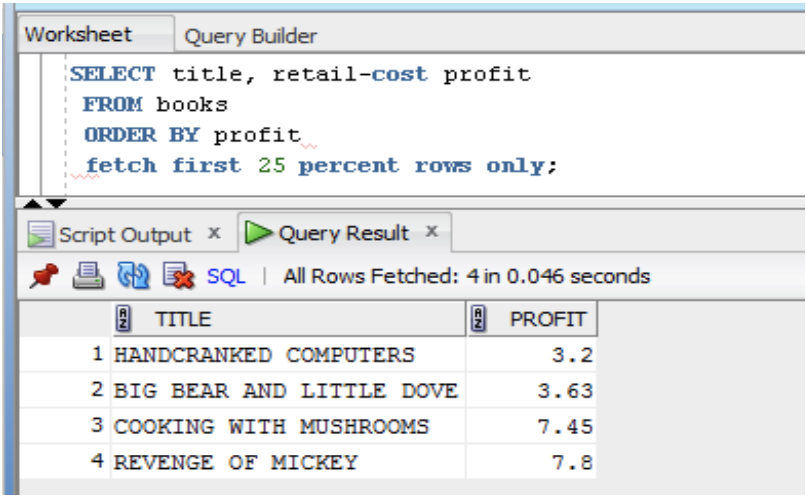
- Oracle 12c introduces a new row limiting clause (percent of rows)
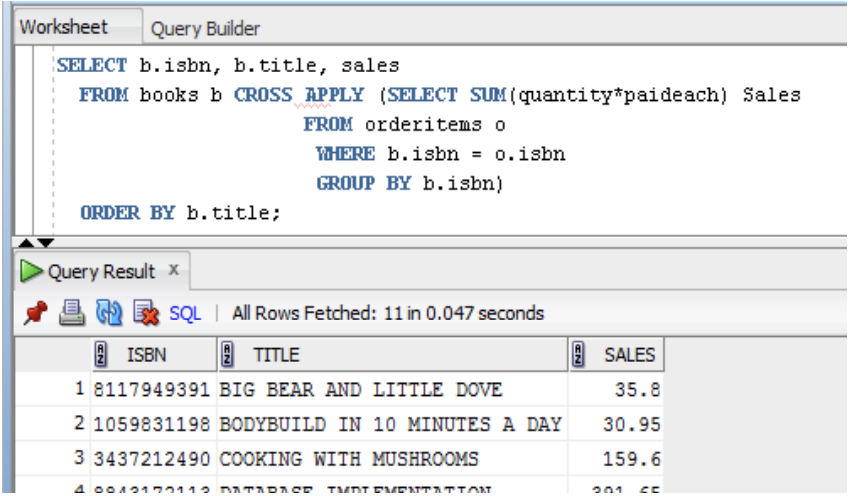
Cross & Outer Apply Joins
- A column of the joining table may be used to product the result set of the inline view
SELECT b.isbn, b.title, sales
FROM books b CROSS APPLY (SELECT SUM(quantity*paideach) Sales
FROM orderitems o
WHERE b.isbn = o.isbn
GROUP BY b.isbn)
ORDER BY b.title;
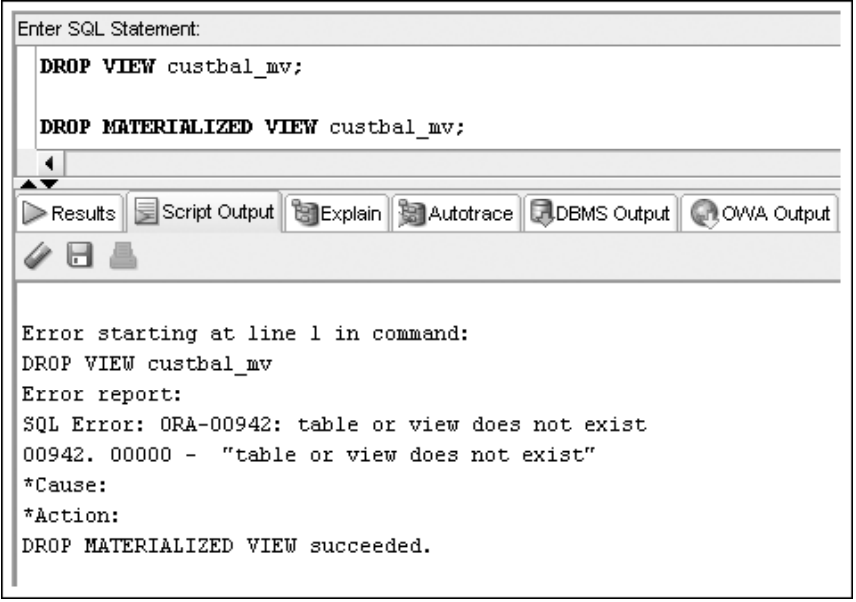
Materialized Views
- Replicate data
- Store data retrieved from view query
- Referred to as “snapshots”
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW custbal_mv
REFRESH COMPLETE
START WITH SYSDATE NEXT SYSDATE+7
AS SELECT customer#, city, state, order#, SUM(quantity*retail) AS Amtdue
FROM customers JOIN orders USING(order#)
JOIN orderitems USING(order#)
JOIN books USING(isbn)
GROUP BY customer#, city, state, order#;
-- CREATE MATERIALIZED succeeded.
Summary
- A view is a temporary or virtual table that is used to retrieve data that exists in the underlying database tables
- The view query must be executed each time the view is used
- A view can be used to simplify queries or to restrict access to sensitive data
- A view is created with the CREATE VIEW command
- A view cannot be modified; to change a view, it must be dropped and then re-created, or the CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW command must be used
- Any DML operation can be performed on a simple query if it does not violate a constraint
- A view that contains expressions or functions, or that joins multiple tables, is considered a complex view
- A complex view can be used to update only one table; the table must be a key-preserved table
- Data cannot be added to a view column that contains an expression
- DML operations are not permitted on non-key-preserved tables
- DML operations are not permitted on views that include group functions, a GROUP BY clause, the ROWNUM pseudocolumn, or the DISTINCT keyword
- Oracle 12c assigns a row number to every row in a table to indicate its position in the table; the row number can be referenced by the keyword ROWNUM
- A view can be dropped with the DROPVIEW command; the data is not affected, because it exists in the original tables
- An inline view can be used only by the current statement and can include an ORDER BY clause
- “TOP-N” analysis uses the row number of sorted data to determine a range of top values
- Materialized views physically store view query results

Leave a comment